A few decades ago it was impossible to really conceptualize smart factories with advanced sensors, robotics, and machine learning algorithms. Well, unless it was in a science fiction movie, where machines take over the world. But here we are, deep in the Industry 4.0 phase!
Instead of relying on human intervention at every step, machines and systems can now communicate, analyze data in real time, and even make data-backed decisions. No, they’ve not taken over the world, but they have created more intelligent, flexible, and efficient production systems.
How did we get here? It has simply been a result of “natural evolution” from past industrial revolutions.
The First Industrial Revolution brought mechanization through steam power. The Second introduced electricity and mass production through assembly lines. The Third saw the rise of computers and automation. Industry 4.0 is taking things a step further by digitally connecting and automating industry processes, from the factory floors to supply chains.
Industry 4.0 overview
So what is Industry 4.0? Industry 4.0, also called 4IR, is the Fourth Industrial Revolution, which is the latest phase of digitization in modern manufacturing.
The phase is characterized by automation and smart manufacturing factories, where machines communicate, learn, and optimize processes. This, in turn, streamlines operations, boosts efficiency, and reduces downtime.
4IR has been made possible by the integration of technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), and cloud computing into the manufacturing process. We’ll dive deeper into key technologies that are collectively driving Industry 4.0 shortly.
Evolution of industrial revolutions
You can’t fully understand how we got to Industry 4.0 without understanding the preceding industrial revolutions that set the stage for it and the impact each one had.
First Industrial Revolution: Mechanization
The First Industrial Revolution, spanning the late 18th century to the early 19th century, started in Britain through the introduction of steam engines and mechanized production.
This led to the shift from manual labor (from humans and animals) to mechanized manufacturing, which significantly increased production capacity and efficiency. The steam-powered machinery revolutionized key industries like textile production, agriculture, and transportation.
Second Industrial Revolution: Mass production
The Second Industrial Revolution began in the late 19th century and continued into the early 20th century.
It brought about mass production through assembly lines and the use of oil, gas, and electric power in manufacturing. Innovations like electricity, internal combustion engines, and more advanced communication channels like the telephone and telegraph completely revolutionized industrial processes.
The assembly line in particular, which was popularized by Henry Ford, enabled large-scale manufacturing, making products more affordable and accessible to consumers.
Third Industrial Revolution: Automation
The Third Industrial Revolution, or the Digital Revolution, started mid-20th century with the introduction of computers, robotics, the internet, and early automation software technologies.
The automation of repetitive tasks in factories and the integration of digital communication technologies paved the way for more sophisticated manufacturing processes.
Fourth Industrial Revolution: Digital transformation
Industry 4.0 has emerged in the past decade or so. The term was popularized by Professor Klaus Schwab, Founder and Executive Chairman of the World Economic Forum in his book The Fourth Industrial Revolution.
However, the Third Industrial Revolution has been setting the pace for it for a while. As such, the 4IR builds on advancements in computation and digital communications with the integration of smart technologies like AI into manufacturing processes.
As we’ve mentioned in our Industry 4.0 definition, this era has ushered in a new age of interconnectedness and automation. It has helped business owners streamline and have oversight over every aspect of their operations. Manufacturers can also leverage real-time data and predictive analytics to boost productivity, improve processes, and drive growth.
Key technologies driving Industry 4.0
As mentioned earlier, Industry 4.0 is powered by advanced digital technologies that enable automation, real-time decision-making, and interconnected industrial ecosystems. Let’s explore four key technologies shaping this revolution in depth.
Internet of Things (IoT) integration
The IoT is a network of interconnected devices that communicate and share data with each other. In an Industry 4.0 context, IoT devices connect machines, systems, and sensors to enable real-time monitoring and control.
For instance, smart sensors on production lines can monitor parameters like temperature, humidity, pressure, and machine performance to detect issues before they lead to downtime.
In addition, connected supply chains and inventory systems can automatically adjust to align with delivery times and product demand. This level of connectivity simplifies production planning and makes industrial processes more responsive and cost-effective.
Siemens, the global industrial powerhouse, leverages IoT in its MindSphere platform. MindSphere connects industrial machinery and equipment to the digital cloud. This makes it easy to analyze real-time data from sensors and devices to improve operational performance.
Big data and advanced analytics
With so many connected devices generating data, from assets to production equipment and IoT-enabled devices, manufacturing businesses need powerful tools to make sense of it all.
Big data and advanced analytics technologies make it easy for manufacturers to process and analyze the massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices to extract valuable insights. These insights drive predictive maintenance, process optimization, and more strategic decision-making.
Rolls-Royce, for instance, leverages big data and data analytics through its innovative Digital Twin technology. Digital Twins are virtual replicas of physical objects, processes, and systems.
Rolls-Royce creates digital twins of their in-service engines, which are comprehensive, data-driven models that mirror real-world performance, condition, and operating environments.
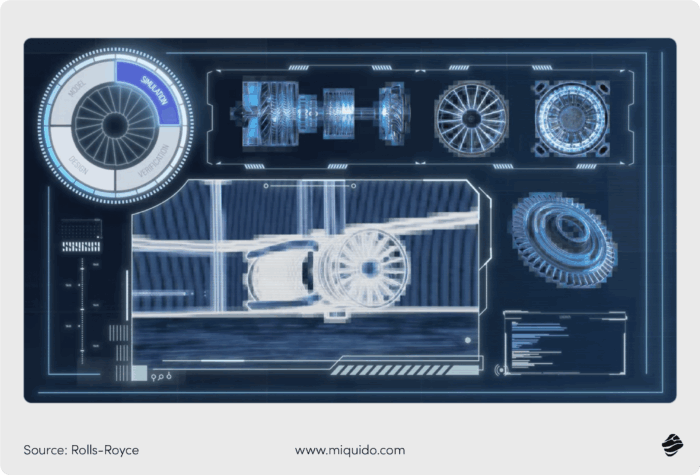
These digital twins enable Rolls-Royce to optimize maintenance schedules, detect problems early, and prevent malfunctions, ensuring engine availability and reliability.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) bring self-learning capabilities to Industry 4.0.
ML algorithms learn from data to improve performance over time, while AI enables machines to perform complex tasks with high precision. Together, these technologies allow machines to analyze patterns, predict trends, automate complex processes, and make intelligent decisions with little to no human intervention.
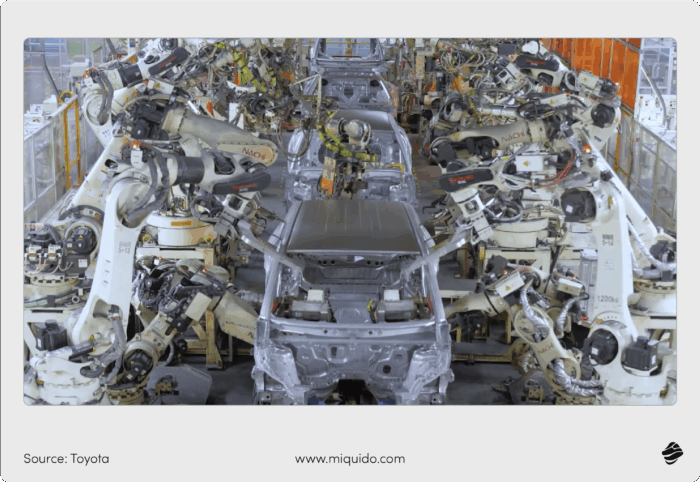
These robots can self-optimize their stamping, welding, and assembly techniques based on real-time data from the production line to ensure higher precision and consistent product quality.
Cyber-physical systems and smart factories
Cyber Physical systems (CPS) merge digital intelligence and physical machinery to help factories operate autonomously with minimal human input. These systems use real-time data and technologies like AI and IoT to create smart factories that self-regulate and automatically respond to changing production conditions and demand.
Bosch’s Nexeed is a great example of a manufacturing system that aligns with CPS principles.

At the Bosch plant in Blaichach, Germany, Nexeed software reads data from over 60,000 sensors to provide real-time insights. These insights support predictive maintenance and reduce machine downtime by 25%.
The software suite includes the Industrial Application System, which connects with several manufacturing applications through a unified dashboard. This connectivity is achieved through a digital twin that collects and homogenizes data, making it easier to process, analyze, and share.
For example, a machine might send a combination of numbers like “1 + 2012-09-25T08:15 + 23.8.” The digital twin interprets this data to generate an alert, like “The coolant temperature at 8:15 a.m. on November 25, 2022, was 23.8°C, 3.8 degrees above the standard operating temperature of 20°C”.
Nexeed also facilitates logistics through an app called Nexeed Intralogistics Execution. The app provides real-time transparency regarding the path of materials from storage to the point of use in production. As a result, it helps plants optimize material flow and workload for logistical assets, boosting efficiency by up to 35%.
Finally, through Nexeed, Bosch plants can combine readings taken from meters and sensors and use the insights to save energy and maintenance costs. The Homburg plant was able to pinpoint leaks, which led to 40% less power consumption and saved them €800,000 a year.
Benefits of implementing Industry 4.0
Let’s explore some of the key benefits of implementing Industry 4.0.
Enhanced operational efficiency
One of the most significant benefits of Industry 4.0 is streamlined operations. Automated systems can perform repetitive tasks with exceptional precision. This reduces human errors and increases productivity.
Predictive maintenance, powered by IoT and big data analytics, also allows companies to anticipate and address equipment issues before they escalate to minimize downtimes and maintenance costs.
In addition, AI-powered systems and devices ensure consistent product quality in shorter periods and with fewer errors.
Real-time decision making
Unlike traditional manufacturing processes that only rely on historical data and reactive strategies, Industry 4.0 technologies provide real-time data insights. These enable businesses to identify patterns and predict future trends, leading to data-driven and proactive business decisions.
For instance, production companies can predict supply chain disruptions, prevent quality defects, and adjust pricing based on market demand. They can also monitor production lines in real time to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies that unnecessarily raise operational costs.
Increased flexibility and customization
Industry 4.0 technologies facilitate mass customization and agile manufacturing processes.
Advanced technologies, like additive manufacturing and AI-driven design solutions, help businesses produce customized products tailored to individual customer preferences. This means companies can meet individual customer demands without sacrificing efficiency or increasing production costs.
For instance, Nike uses automated manufacturing and AI to create custom sneakers tailored to individual foot shapes. One of their notable projects is the Nike A.I.R. (Athlete Imagined Revolution) line, which features 3D-printed sneakers.
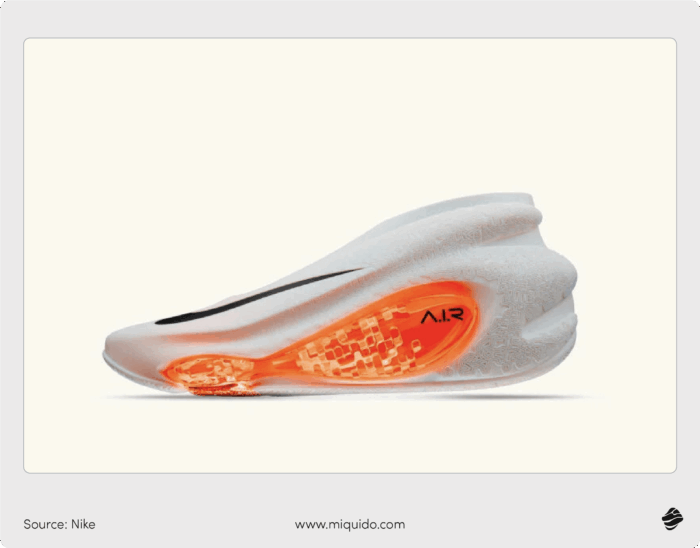
The agile manufacturing processes allow businesses to quickly adapt to new product designs and production requirements. For instance, AI-driven production lines can switch between product variations instantly without manual reconfiguration. This flexibility reduces lead times and improves time-to-market.
Improved product quality and reduced downtime
AI-powered quality control, automated defect detection, and data-driven optimization ensure consistent product quality and reduced downtimes.
Machine learning algorithms make it possible to detect defects and anomalies in real time. The AI-powered systems can use sensor data to detect defects faster than human inspectors.
Once the issues are identified, the interconnected smart systems can adjust production parameters in real-time to reduce defects and waste.
Additionally, predictive maintenance helps prevent equipment failures, which results in fewer downtimes. The lack of production disruptions goes a long way in ensuring consistent product quality.
Challenges in adopting Industry 4.0
While Industry 4.0 offers great benefits, it also poses some challenges. Here are some of the potential obstacles businesses might face when transitioning to Industry 4.0.
Data security and privacy concerns
The more manufacturing businesses embrace Industry 4.0, the more vulnerable they become to cyber threats.
In fact, in 2023, the manufacturing sector suffered 25.7% of the cyberattacks among leading industries globally. This was nearly a quarter of the total cyber attacks, making it the highest share of cyberattacks among key industries like finance, insurance, healthcare, energy, and retail.
Cybersecurity risks like hacking and data breaches that lead to industrial espionage or supply chain attacks compromise sensitive industrial data. To avoid falling prey to these risks, implement robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption, firewalls, access controls, and training employees to protect their networks and data.
Conducting regular security audits will also help identify vulnerabilities beforehand. You can use generative AI in cybersecurity to strengthen your systems. AI-powered solutions can automatically analyze data at scale, identify threats, and recommend solutions.
Additionally, since cloud-based operations often involve third-party vendors, adhere to data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Integration with legacy systems
Integrating Industry 4.0 technologies with legacy systems is the other key challenge.
Many traditional manufacturing facilities still rely on outdated infrastructure that may not be compatible with modern digital technologies. Replacing entire production lines with new Industry 4.0-ready equipment is not an option for most due to the high price tags.
To ensure interoperability between old and new systems, use Industrial IoT gateways to connect older machines to digital systems. Also, adopt middleware solutions like CIMCO Software, KEPServerEX, and IBM Integration Bus (IIB) that bridge the gap between old and new technologies.
In addition, instead of full replacements, gradually integrate smart technologies into existing systems to minimize disruption. You can also partner with technology vendors and manufacturing software development companies like Miquido to develop customized integration solutions tailored to your unique business needs.
Skill gaps in the workforce
Industry 4.0 requires a skilled workforce that can comfortably manage and operate various technologies and digital systems. However, there is a shortage of workers skilled in these advanced technologies. Also, Industry 4.0 is constantly evolving, so it requires a workforce that is willing to learn and adapt quickly.
To fill these skill gaps, actively invest in upskilling and reskilling employees. You can provide company training programs with hands-on training opportunities, like workshops or simulations, to help employees gain practical experience with new technologies.
You can also create a pipeline of skilled workers by partnering with universities and technical schools to develop courses that align with Industry 4.0 requirements.
High initial investment costs
Implementing Industry 4.0 technologies requires significant initial investment, which creates a financial barrier for some manufacturing businesses.
But while the initial investment may be high, you must also consider the return on investment (ROI) and other long-term benefits that make the adoption worthwhile. For instance, adopting 4IR will boost efficiency, reduce downtimes, and improve product quality. This ultimately lowers the cost of production and raises your profits.
You can use the phased approach to implementation to adopt Industry 4.0 in a more financially manageable way. Start with small, high-impact projects and gradually scale up to larger parts of your manufacturing process. Alternatively, you can introduce the Industry 4.0 tech plant-by-plant.
Future trends beyond Industry 4.0
As businesses continue to embrace Industry 4.0, the next phase of industrial transformation is already shaping up. Here are some of the future manufacturing technology trends that will define the future of manufacturing and industrial processes.
Emergence of Industry 5.0
Industry 4.0 has been all about automation, AI, and smart factories, but Industry 5.0 will bring humans back into the loop. Instead of fully automated production, the next phase will prioritize human creativity and intuition, personalization, and ethical AI integration.
Manufacturers will continue to customize products based on individual consumer preferences with human input for more personal and meaningful products. AI-driven systems will also fully incorporate ethical considerations to eliminate bias in the manufacturing and industrial processes.
Human-machine collaboration enhancements
The biggest concern in the Industry 4.0 phase has been about technology taking human jobs. While it did not take the jobs, the Fourth Industrial Revolution has changed the nature of the manufacturing workforce through collaborative intelligence.
Therefore, in the future, we will see cobots (collaborative robots) with more intuitive and safe features continue to handle repetitive tasks, while humans focus on innovation and customization.
AI systems will also continue to assist human workers by providing valuable insights, recommendations, and support that enhance human productivity and capabilities.
Sustainable and resilient manufacturing practices
Due to the growing environmental concerns, the future of manufacturing will be defined by sustainability and resource efficiency. As such, manufacturers will embrace green technologies, circular economy principles, and energy-efficient production methods.
Companies will continue to use eco-friendly materials, like biodegradable plastics and sustainable packaging solutions to minimize their environmental footprint. They will also depend more on renewable energy and IoT sensors to monitor and optimize energy usage.
Finally, more manufacturing factories will embrace recycling or reusing materials to minimize industrial waste.

![[header] what is industry 4.0](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/header-what-is-industry-4.0.jpg)


![[header] case study b2b system development and product configurator implementation
in industry 4.0](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/header-case-study_-b2b-system-development-and-product-configurator-implementation
in-industry-4.0-432x288.jpg)

![[header] exploring the key benefits of ai in manufacturing industry](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/header-exploring-the-key-benefits-of-ai-in-manufacturing-industry-432x288.jpg)
![[header] woodworking automation – how joinery industry is growing with digital transformation which is right for your project](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/header-woodworking-automation-–-how-joinery-industry-is-growing-with-digital-transformation-which-is-right-for-your-project-432x288.jpg)