We are on the verge of a technological revolution involving expanding Artificial Intelligence, Machine learning capabilities, Natural Language Processing, and blockchain development advancements.. At the same time, the conversion to Web 3.0 implies inevitable social, economic and business changes. Open-source software, the Internet of Things, and open access scholarly outputs are just a few glimpses of a wide-ranging transformation taking place right before our eyes.
The following analysis will allow you to understand the basic assumptions of Web 3.0 and discover some predictions regarding its business impact. In the overview of different business sectors (including fintech, e-commerce and healthcare), we’ve included industry recommendations and suggestions on using Web 3.0 as a competitive advantage.
After all, we want you to feel that you should not be afraid of the paradigm shift. You just need to understand and use the change in your favour. Let’s start from the beginning and trace the evolution of the web: from readable Web 1.0, through social Web 2.0, to user-centred Web 3.0.
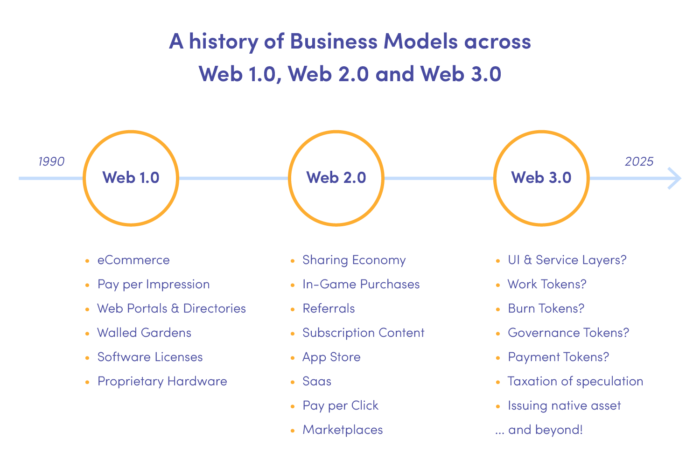
Web 1.0, Web 2.0, Web 3.0
Web 1.0 is the first web implementation introduced by British physicist and computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee in 1989. The worldwide project of information connection networks was initially based on hyperlinks that allowed for the non-linear movement based on user preferences and needs.
The first “readable” phase of the World Wide Web resembled an online library or news feed and provided little interaction between users and websites. The second generation of the web, defined circa 2005, has allowed the creation of global communities with shared interests and interaction with other users. Hence the colloquial term Web 2.0 – Social Web, a “writable” platform dominated by social media, real-time information sharing and self-publishing tools such as WordPress and blogs.
Over the years, Web 2.0 has revealed the hegemony of large corporations that saw a business opportunity in collecting and processing the personal data of Internet users. The latest stage in technological evolution, is a project that responds to the need to transform into a transparent, user-centred, safe and decentralized web.
User-centric model of Web 3.0
There are many terms related to the idea of Web 3.0: “semantic web technologies”, “3D Web”, or “the Spatial Web”. Each serves as a fragmentary description of a still-evolving successor to Web 2.0. Regardless of the name, the primary objective of the next generation web remains the same: to restore the web to its users.
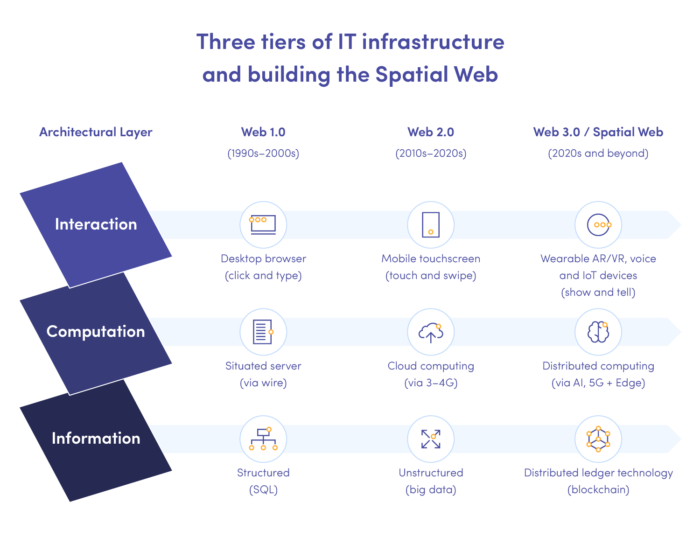
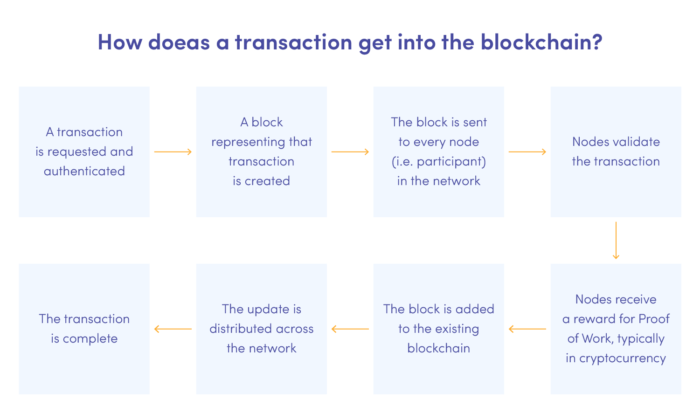
At the information management level, distributed ledger technologies such as blockchain are fundamental for Web 3.0. Blockchain technology is a decentralised, anonymous, immutable record of all network operations, ensuring data integrity and security. Hence, it forces open ecosystems with no central moderation, where business intermediaries are deprecated in favour of increasing the value of a service or product. Thanks to its properties, blockchain may be used in any industry where data transfers occur.
3 universal business values in the Web 3.0 era
The semantic web is a phenomenon bordering on science and ethics. Hence before we take a closer look at specific industries, it is essential to discuss the universal business values that will become key in the era of Web 3.0:
1) Transparency
Transparency in brand-client relations with the highest respect for user privacy. Allow your users to decide how you process and access data.
2) Innovation
Try to respond to the needs of your users as quickly as possible, using emerging technologies and tools exploiting the metaverse convergence of the digital and physical worlds.
3) User-first approach
Your product must bring real value to your users and make a positive social impact. User-oriented approach, open collaboration, community – keep these keywords in mind.
Web 3.0 is a technology at the service of wide-ranging social, political and economic change. But what does this seemingly abstract change mean for specific business sectors?
Web 3.0 and fintech
Web 3.0 is a permissionless network that requires no overseeing governing body. Open financial protocols enable the performance of peer-to-peer actions secured by blockchain technology.
Therefore, for the fintech app development industry, Web 3.0 can indicate significant competitive advantages, including:
- uninterrupted service – when storing data at decentralised, distributed nodes, fintech organisations will be able to optimise their expenditures on unexpected server errors or seizures
- faster transactions – digital assets and peer-to-peer digital services (e.g. payments, loans, BNPL, lendings) involving no third-party beneficiaries are better secured
- automated data processing – AI and ML solutions allow organisations to quickly adapt to evolving user needs, leading to the ongoing improvement of the customer journey
- mutual trust – due to the decentralised data architecture, each fraction has access to the same information, which prevents data from being modified or hacked. At the same time, end-users always have full ownership and control over their data.
- new opportunities – Web 3.0 solutions can resolve many spatial, infrastructure, or security constraints, providing new opportunities for investors, e.g., introducing innovative financial services in the most demanding markets.
The Web 3.0 fintech transformation has already begun. Currently, the advanced technological improvements are used in a number of cases, including:
- reducing call centre demand – The Royal Bank of Canada employed deep reinforcement learning to reduce client calls
- fraud detection improvement – Thanks to collaborative multi-party GPU computing, BNY Mellon improved its fraud prediction accuracy by 20%
- decentralised finance lending services – Bitcoin Suisse has recently begun offering contracts based on the ETH collateral, allowing clients to mint and borrow the Liquidity Dollar stablecoin
If you want to listen to more real-life business experience, you might be interested in our AI Waves webinar. During the panel discussion, you’ll meet leaders and experts from the banking and fintech industries, who’ll speak about the actual values of the Web 3.0.

Web 3.0 and e-commerce
E-commerce is evolving with every web iteration. The first e-commerce platforms were a hybrid of physical and digital shops based on early pick-up & collect solutions. The monopolised e-commerce 2.0 model involves more interactive solutions, such as product recommendations or order management.
E-commerce 3.0 aims to build an open, no-middleman and entirely customer-oriented economy. Hence, while considering the revamp of the digital shopping experience, it might be important to consider the following features:
- ML & AI-based customisation – Adjusting the product or the offer to the individual customer needs is likely to improve the CLV and the product-market fit, as well as partially replace short-term performance marketing efforts
- tailor-made subscription models – Flexible subscription models, entirely automated within the blockchain, allow companies to increase customer loyalty, ensure a higher customer retention ratio, and secure long-term brand building
- safe P2P payments – Blockchain-secured P2P transactions are safer, faster, and less subject to third-party threats
- data protection & privacy – According to M. Damlapinar, eRetail Director at L’Oréal, blockchain will make it easier for e-commerce stores to build effective authentication mechanisms and encrypted digital identities for improved identity management
- XR solutions – The immersive shopping experience, e.g. placing products to examine in real space or virtual try-on, is an increasingly popular trend which reflects the digital/physical convergence of Web 3.0
Ready to boost your eCommerce business? Read about our custom eCommerce development solutions!
Web 3.0 and healthcare
There is no doubt that the pandemic has contributed to the rapid digitisation of the healthcare industry over the past two years. As a result, access to specialist care has become more available, constant and safe.
The healthcare sector in the Web 2.0 era is based on telemedicine, health forums, and telehealth platforms that enable fast and universal access to many services. However, the actual price users pay for this convenience is controversial.
But setting aside these gains for a minute, most Web 2.0-based healthcare is still about creating information silos, disregarding patients’ ownership of their own data and rushing to centralise, mainly to benefit the shareholder. In the Internet’s latest avatar, Web 3.0, everything functions around individuals instead of centralised companies, because it is built using open-source software by a public community of contributors.
A. Rungta
How Web 3.0 Might Revolutionise Healthcare
So the question is, how can Web 3.0 become a cure for the healthcare industry?
- patient-owned electronic health records (EHRs) – Sensitive data spread across distributed ledgers remains immutable and private
- improvement of preventive care – The further development and customisation of personal healthcare apps and wearable technology increases patient self-management. Prevention is better than cure and benefits both patients and the healthcare system.
- better access to health related information – The semantic character of Web 3.0 enables the better organisation of EHRs into open information architecture. It allows for quick insight into the patient’s treatment history in case of an emergency and an increased flow of expert knowledge.
- improved verifiability – The encrypted health records require no intermediaries. They can be confirmed at the source and yet efficiently verified via DeFi tools.
Summary
For many companies, entering the Web 3.0 reality will undoubtedly mean the need to reformulate business processes or create new business models from scratch. Adaptation will not be easy, but there is no doubt that in the long run, understanding the specifics of a transparent semantic web will enable businesses to develop a competitive advantage that will remain impossible to make up for those who decide to lag behind.
If you are still unsure how to take advantage of this opportunity, don’t hesitate to reach out for a personalised recommendation.