Healthcare stands to gain the most from technological advancements, especially in regions like the USA and Europe, where aging populations put increasing pressure on medical systems. By integrating technology, we can minimize unmet medical needs and better handle the growing demand for medical services.
While not every task in healthcare can be replaced by tech, the right software can alleviate the workload on medical staff, resulting in time and cost savings. This leads to more efficient doctors, fewer administrative errors, and improved patient care. From streamlining processes to enhancing treatment outcomes, healthcare software plays a crucial role in supporting medical professionals.
In this article, we’ll explore the most common types of healthcare software, their functions, features, and challenges. Whether standalone systems or part of an integrated platform, these tools are transforming the healthcare landscape. Let's take a look at custom systems and solutions provided by top healthcare software companies, understanding the challenges they face.
Electronic Health Records (EHR) Software
Keeping track of a patient's medical history is essential to successful therapy. Traditional health record systems do not facilitate this, making data exchange much more challenging, error-prone, and insecure. The traditional method involves staff at one medical facility copying or printing the patient's records, which are then sent to the requesting facility.
In an ineffective healthcare system, this creates various risks and places a lot of responsibility on the patient. Paper documents can easily be lost, and the data may be exposed to unauthorized third parties. Furthermore, maintaining complete records and exchanging them between institutions can be a potential obstacle to effective treatment.
Electronic health record software tackle these issues at once, improving data management and access. Medical units can easily keep track of documentation and seamlessly exchange it in electronic health records form. Today, EHR is an essential foundation of healthcare industry globally.
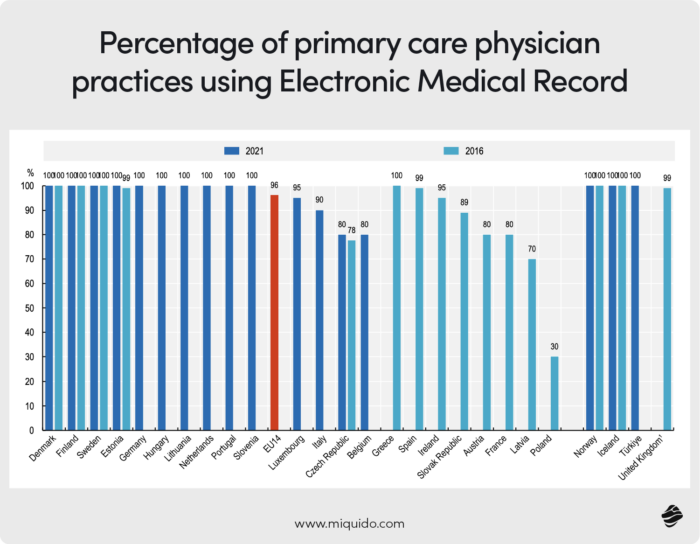
According to the Health at a Glance: Europe 2022 report, by 2021, nearly 96% of primary care doctors across 14 different countries were using electronic medical records (EMR) in their practices. The pandemic was an impulse for innovation, with 10 out of 14 EU countries declaring plans to develop and integrate EHRs into the wider health ecosystem.
Electronic Health Records Software challenges
Ensuring data security and patient privacy in compliance with regulations like HIPAA is a major concern, as EHR systems are prime targets for cyberattacks.
Adapting EHR Systems to HIPAA & GDPR
Regulatory compliance is essential for EHR, considering the confidential nature of patient data. Both GDPR (EU) and HIPAA (US) impose strict data privacy and security requirements, but they have different scopes and focuses. Personal health record software adjusts to them by ensuring patient data is stored, accessed, and transmitted securely. They also need to offer patients control over their information and provide auditability for healthcare organizations.
- Access Control: Role-based access ensures only authorized staff can access sensitive patient data.
- Encryption: EHR software uses encryption for data in transit and at rest, complying with HIPAA's security rule and GDPR's data protection requirements.
- Audit Trails: Comprehensive logging and monitoring of data access and changes help meet accountability requirements.
- Patient Rights:
- GDPR: EHR systems provide tools for patients to access, correct, delete, and export their data.
- HIPAA: EHRs offer access and amendment features but without the "right to be forgotten" or data portability.
- Breach Notifications: EHR platforms are designed to quickly detect and report breaches, fulfilling GDPR’s 72-hour and HIPAA's notification requirements.
GDPR and HIPAA Comparison
| Aspect | GDPR | HIPAA |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Applies to any organization handling personal data of EU citizens, globally. | Applies to U.S. healthcare providers, insurers, and their business associates. |
| Data Type | Covers all personal data (including health data). | Focuses specifically on Protected Health Information (PHI). |
| Patient Rights | Right to access, rectification, erasure, restriction, and portability of data. | Right to access and amend health records; no right to erasure or portability. |
| Consent for Processing | Explicit patient consent or other lawful basis required for data processing. | Consent is needed primarily for sharing data outside treatment, payment, or operations. |
| Breach Notification | Must notify within 72 hours of a breach to authorities and individuals. | Must notify affected individuals and HHS, with media notification in certain cases. |
| Security Standards | Requires data encryption, access control, and accountability through policies. | Enforces technical, administrative, and physical safeguards for PHI. |
Practice Management Software
Healthcare systems worldwide are overburdened, impacting the accessibility of treatment and the well-being of patients. The State of Health in the EU Synthesis Report 2023 shows that in the EU, 18% of patients report unmet healthcare needs.
The root cause of this situation is the shortage of medical specialists and infrastructure, but inefficient back-office operations also play a big role. Streamlining administrative tasks might not fill the professional gap, but it could reduce bureaucracy, making it easier for patients to receive timely and effective treatment.
Practice management healthcare software enables healthcare providers to achieve that goal by facilitating scheduling, billing, and patient management. Addressing administrative challenges is often a major obstacle for patients, particularly migrants or those living in geographically excluded areas. Digital healthcare solutions can remove these barriers, enabling more inclusive access to healthcare.
Patient Scheduling
- Appointment Scheduling: Allows for easy scheduling, rescheduling, or cancellation of patient appointments.
- Automated Reminders: Sends reminders to patients via SMS, email, or phone calls to reduce no-shows.
- Calendar Management: Provides a calendar view for tracking multiple providers' schedules, managing availability, and preventing double-booking.
Patient Registration & Demographics
- Electronic Patient Registration: Enables patients to fill out their personal, demographic, and insurance information electronically.
- Patient Database Management: Stores and organizes patient demographics, medical history, contact details, and insurance information.
Billing and Claims Management
- Insurance Verification: Verifies patients' insurance coverage in real-time before appointments.
- Billing & Invoicing: Automates billing processes, including generating invoices for patients and insurance providers.
- Claims Processing: Submits claims electronically to insurance companies, tracks claim status, and handles denials.
- Revenue Cycle Management: Manages the entire revenue cycle from patient registration to final payment, helping to track and improve cash flow.
Medical Coding & Documentation
- ICD/CPT Coding Support: Supports the latest medical coding standards (ICD-10, CPT, etc.) to ensure accurate coding of diagnoses and procedures for billing purposes.
- Code Validation: Automatically checks for errors in coding, reducing claim rejections.
Reporting and Analytics
- Financial Reporting: Generates reports on practice financials, including revenue, expenses, and accounts receivable.
- Patient Flow and Utilization Reports: Provides insights into patient volume, scheduling efficiency, and resource utilization.
- Claims and Denial Reports: Tracks claim approvals, denials, and resubmission rates to optimize billing processes.
Electronic Health Records (EHR) Integration
- EHR Synchronization: Integrates with EHR systems to sync patient medical records with administrative and billing data.
- One-click Access to Medical Records: Allows practice staff to quickly access patient records during scheduling or billing activities.
Patient Communication & Portal
- Patient Portal: Allows patients to access their medical records, view lab results, schedule appointments, and communicate with providers online.
- Secure Messaging: Facilitates secure communication between patients and healthcare providers, ensuring compliance with privacy laws.
Document Management
- Electronic Document Storage: Stores important patient documents such as consent forms, referral letters, and insurance documentation electronically.
- Document Scanning & Upload: Allows for scanning and uploading of physical documents into the system.
Multi-location Support
- Multi-location Management: For practices with multiple locations, the healthcare software allows centralized management of operations, including patient data, billing, and scheduling.
- Provider Assignment: Enables easy assignment of patients to different providers across locations.
Task & Workflow Automation
- Task Management: Tracks administrative tasks like patient follow-ups, prescription refills, or lab result reviews.
- Workflow Customization: Customizes workflows based on practice needs, from patient check-in to billing and follow-up.
Inventory Management
- Supply Tracking: Manages inventory levels for medical supplies, ensuring stock availability and preventing shortages.
- Order Management: Facilitates ordering and reordering of medical supplies and equipment.
Payment Processing
- Credit Card Processing: Integrates with payment gateways to process patient payments (in-person and online).
- Payment Plans: Allows practices to set up and manage payment plans for patients needing financial assistance.
Referral Management
- Tracking Referrals: Manages patient referrals to specialists or other healthcare providers and tracks referral status.
- Referral Reporting: Generates reports on referral sources, helping practices analyze referral patterns.
Practice Management Software challenges
Integrating practice management software with existing systems, such as EHRs or billing platforms, is a frequent obstacle. This interoperability issue can result in inefficient workflows and delays in administrative processes.
Telemedicine Software
The rise of telemedicine software was driven by the COVID-19 pandemic. Although telemedicine existed before, this event led to its rapid adoption globally. Both public and private healthcare providers established new standards in telemedicine that have been maintained beyond the pandemic.
The adoption pace varied by country. In the U.S., many states, such as Texas, saw significant increases in telemedicine services, especially in Medicaid programs (Texas Telemedicine Report). In Asian countries like Singapore, India, and Indonesia, telemedicine healthcare software became part of governmental strategies to improve accessibility in urban areas. Platforms like Doctor Anywhere in Singapore serve as blueprints for other innovations worldwide, setting new healthcare mobile apps trends.
While in some cases telemedicine software happens to be custom, private healthcare units also rely on SaaS model, working with healthcare software providers like Amwell or Teladoc. Usually, it contains the following features:
- Video Consultation Tools: High-quality video calls for patient-provider consultations.
- Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM): Integration with devices that track patient vitals (e.g., heart rate, blood pressure).
- Scheduling & Appointment Management: Easy scheduling, rescheduling, and cancellation options.
- Patient Portal Access: A secure portal for patients to view records, prescriptions, and test results.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) Integration: Synchronization with patient medical history for seamless access.
- Secure Messaging: HIPAA-compliant messaging for secure communication.
- Billing & Payment Processing: Tools for generating bills and processing payments.
- Prescription Management: E-prescription capabilities for remote medication prescriptions.
- AI & Machine Learning Tools: Automated support features like appointment reminders, health monitoring, and diagnosis support.
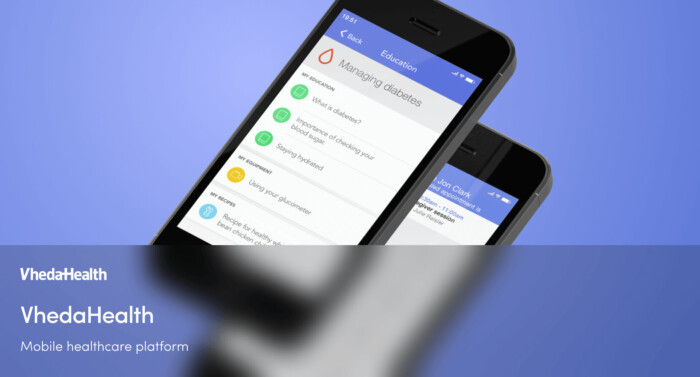
Innovative remote health management
Vheda Health partnered with Miquido to develop a cutting-edge remote disease management and monitoring platform that balances advanced technology with human-centered care. The solution supports interventions for type 2 diabetes, congestive heart failure, and weight management. Through the app, personalized care plans are created using curated data, connecting patients with care teams tailored to their needs. Weekly live video meetings between patients and their care teams provide ongoing support.
Miquido designed and developed mobile applications for iOS and Android, a web application, and an administrative panel, delivering a comprehensive solution for Vheda Health’s vision of remote patient care.
Medical Imaging Healthcare Software
Being essential element of today's diagnostics, medical imaging software enables healthcare providers precisely locate health issues and measure therapy progress. Such systems collect images by converting raw data collected from imaging devices like MRI, CT, and ultrasound scanners into readable and interpretable digital images.
Medical imaging software must integrate with a variety of hospital systems, particularly PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems) and EHR (Electronic Health Records), to ensure seamless sharing and access to images. This integration allows healthcare providers to retrieve, view, and analyze medical images within the context of a patient's medical history and treatment plans. Additionally, the software interfaces with radiology equipment for real-time image capture, as well as with 3D reconstruction and diagnostic tools to enhance interpretation.
The Technological Advancements in Medical Imaging Software
Modern medical imaging systems have advanced significantly in recent years, with innovations like AI-powered diagnostic tools that assist radiologists in detecting abnormalities such as tumors or fractures. Cloud-based platforms now allow for easier storage, sharing, and collaboration between healthcare providers across locations, improving patient care efficiency. Technologies like machine learning and deep learning are increasingly used for image analysis, automating the identification of patterns that may not be visible to the human eye.
3D and 4D imaging have also improved, enabling detailed anatomical views and real-time motion tracking, particularly in cardiology and obstetrics. Innovations like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are being used to guide complex surgeries with greater precision, providing interactive views of the patient’s anatomy. These technologies have dramatically increased the accuracy and efficiency of diagnostic imaging, transforming both routine diagnostics and complex medical procedures.
Medical Imaging Software challenges
Data storage and retrieval is a major challenge with medical imaging software due to the massive file sizes of high-resolution images like MRIs and CT scans. Managing this data efficiently, while ensuring quick access for diagnosis, can strain hospital IT systems, especially when dealing with cloud storage and data security concerns.
Healthcare Customer Relationship Management Software
While the systems mentioned above both function in public and private medical sphere, healthcare CRMs tend to be a domain of the latter, as it can drive significant profit. It gathers patient data, which later can be used for developing customer engagement strategies and improving customer journey.
The data gathered can also serve for personalization purposes. Having integrated CRM data pipelines with the app dedicated for customers, the medical companies can increase conversion rates, driving sales of the healthcare package deals and personalized price plans. If implementing their CRM, the medical companies can reach out for custom healthcare software development. Otherwise, some popular SaaS providers offer specialized medical modules (for instance, Salesforce Health).
Healthcare CRM Software challenges
Ensuring patient engagement while maintaining compliance with privacy laws like HIPAA and GDPR is a key challenge for healthcare CRMs. Balancing personalized communication with strict data privacy requirements can be difficult.
Medical Billing Software
Medical billing healthcare software is essential for managing patient billing, claims processing, and payment tracking in healthcare industry. Its key components include:
- claims management, which helps submit claims electronically to insurance companies;
- patient invoicing, which generates and tracks bills; payment processing to handle patient and insurance payments;
- denial management for resolving rejected claims;
- reporting tools that provide insights into revenue cycles.
The software should integrate with PACS, EHR systems, and accounting platforms, providing a seamless experience from patient care to billing. Additionally, it should support ICD-10 coding and HL7 standards for communication between healthcare applications, ensuring accurate and timely claims processing.
Medical Billing Software: US vs EU Comparison
In the US, medical billing healthcare software is highly complex due to the multi-payer system involving numerous private insurers and public programs like Medicare and Medicaid. It emphasizes insurance claims submission, coding compliance (ICD-10, CPT), and integration with HIPAA standards.
In contrast, the EU typically operates under single-payer or government-funded healthcare systems, where billing is less focused on insurance claims and more on direct reimbursement from government agencies. The structure in the EU is thus simpler, focusing on fewer billing entities and fewer compliance issues regarding private insurance providers.
Medical Billing Software challenges
Staying compliant with changing insurance policies and healthcare regulations is the primary challenge for medical billing software. The complexity of insurance claims, coupled with evolving coding standards like ICD-10, can lead to claim rejections or delays if not properly managed, resulting in lost revenue for healthcare providers.
Pharmacy Management Software
Having entirely different needs than the healthcare units, pharmacy management software requires a particular set of features, with strong emphasis on inventory management and regulatory compliance. Typical set of pharmacy management software features consists of:
- Inventory management: Monitoring and ordering medications.
- Transaction handling: Managing sales, payments, and invoices.
- Patient records: Registering patients and managing their medical histories.
- Report generation: Creating reports on sales, inventory, and transactions, supporting financial analysis and process optimization.
- Insurance integration: Connecting with insurance systems, national drug reference databases, and managing reimbursement processes, simplifying the handling of patients using drugs reimbursed by the National Health Fund.
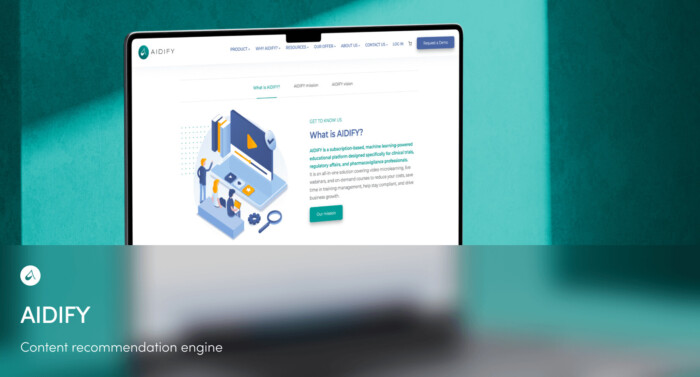
Learning revolution in pharmacy
AIDIFY is a forward-thinking startup focused on enhancing training within the pharmaceutical industry, especially in areas requiring strict legal compliance like pharmacovigilance, clinical trials, and regulatory affairs. Its subscription-based platform offers personalized, automated, and standardized learning through video microlearning, live webinars, and on-demand courses tailored to individual user needs.
In partnership with Miquido since 2020, AIDIFY has leveraged a course recommendation engine to power its Learning Experience Platform (LEP). This engine supports users in achieving specific competency goals by suggesting relevant courses, which enhances engagement, reduces churn, and fosters customer loyalty, establishing a strong base for AIDIFY's long-term success.
Changes in pharmacy management software
The introduction of the e-prescription system in Poland imposed new requirements on both pharmacies and healthcare software providers. Pharmacies had to adapt their systems to handle the new model for prescribing and processing prescriptions, which required modernization of Pharmacy Management Software (PMS) and staff training. A key requirement became integration with the P1 system, as well as compliance with data protection regulations, including GDPR. The e prescribing software must also handle updates related to reimbursement and communication with the National Health Fund (NFZ).
Pharmacy Management Software challenges
New processes for electronically transmitting and approving prescriptions require IT solutions with e-prescribing software modules capable of handling real-time data flow. Potential integration with European systems necessitates scalable solutions that enable linking with HDSI (eHealth Digital Service Infrastructure), facilitating the exchange of e-receipts between the EU countries.
Hospital Management Software
Hospital management software often combines the modules listed above, enabling the medical units to navigate complex processes of managing treatment plans, billing, and processing crucial health data gathered by medical personnel, through exams and devices.
The complexity of hospital management requires well-thought out, scalable architecture that facilitates integrations and enables seamless data flow from numerous devices.The NHS in England reports millions of diagnostic imaging tests annually, with around 44.5 million procedures conducted in 2022. This translates to an average of 120,000 scans per day across the system and hundreds to thousands per day in larger hospital units.
Imagine the load generated by such an intense flow of data. Medical equipment, medical practices, hospital wards are all sources of It needs to be properly categorized, archived, and secured. Patient information, their needs, treatment plans, and medication dosages must reach the correct healthcare staff. Add to this the data related to people entering and leaving the facility, their insurance details, and potential billing processes. That's quite a lot to process, right?
A typical hospital management software links all these areas, including such modules as:
- Patient Admissions and Discharge Management: Streamlining the admission, transfer, and discharge processes.
- Bed Management: Efficient allocation and monitoring of hospital beds.
- Inventory Management: Real-time tracking of medical supplies, equipment, and medications.
- Staff Scheduling: Automation of staff rosters and scheduling shifts.
- Billing and Financial Management: Integrated billing systems that handle inpatient, outpatient, and emergency services.
Hospital Management System challenges
Aside from effective integration, security remains the main challenge for implementing a hospital management system (HMS), especially with the growing frequency of cyberattacks in the healthcare sector.
A stark example of this risk occurred at Centrum Zdrowia Matki Polki (CZMP), one of Poland’s leading specialized healthcare units, which faced a cyberattack in November 2022. The ransomware attack severely disrupted operations, leading to temporary shutdowns of key systems, including scheduling, medical records access, and patient data management.
To mitigate risks, hospitals must continually evolve their cybersecurity protocols, invest in staff training, and ensure swift response capabilities to cyber incidents. However, the architecture of their software and the strong protection of numerous endpoints are also essential, and that's more challenging due to the complex integration of medical devices, legacy systems, and patient data. Without robust security measures at every endpoint, hospitals remain vulnerable to cyberattacks that could disrupt services and compromise sensitive information.
Streamlined healthcare communication
Pando addresses the challenge of inefficient communication among healthcare practitioners, enhancing information flow within hospitals and freeing up time for doctors and nurses to focus on patient care.
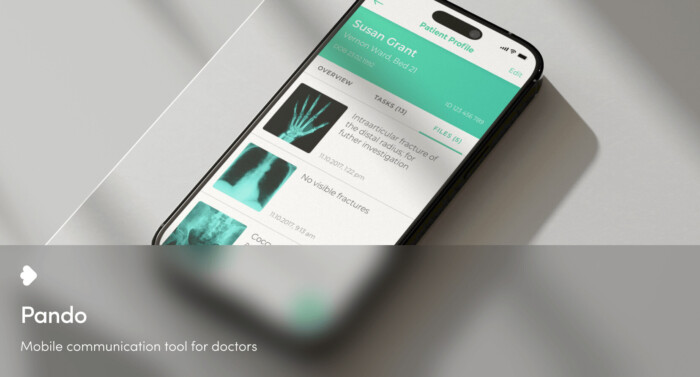
Miquido developed Pando with a user-centered design that helps healthcare staff save up to an hour daily, optimizing their workflow. The solution includes mobile UX/UI design, web and mobile development, and is built for both Android and iOS platforms, delivering a seamless experience across devices.
Wearable and IoT-Connected Devices
IoT has revolutionized daily life in many homes and has also elevated the management of medical facilities. The integration of smart devices enables efficient collection of patient health data and effective analytics.
MRI machines, CT scanners, ventilators, heart monitors, infusion pumps, ultrasound devices, patient monitoring systems, and smart hospital beds — all of these pieces of medical equipment can be integrated with medical equipment management software and a whole healthcare system, feeding data into medical databases.
Medical facilities can also monitor data in real-time and remotely make decisions or initiate actions (e.g., increasing medication dosage). These capabilities alleviate the workload for staff, especially in larger facilities, while also helping protect patient health more effectively.
Diagnostics also benefit from using intelligent devices, especially if they are wearable. These devices can collect health data during recovery or diagnosis, such as heart rate or blood glucose levels, supporting healthcare professionals in decision-making processes. Such remote patient monitoring can increase therapy success rates and cut the lenghty diagnosis, especially in hard to detect diseases. The data flow can be integrated with health tracking apps which enable patients to actively monitor and enhance their therapy.
Are you more interested in the client-side of healthcare software? Dive into our guide to mobile apps in the healthcare industry, where you can find the essential features and practices for delivering a successful solution that will drive engagement and enhance efficiency.








![[header] how ai is used in healthcare](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/header-how-ai-is-used-in-healthcare-432x288.jpg)
