Humans have dreamt about creating intelligent machines since ancient times – but only made the first attempts to actually do this in the early 50s. Now, in 2025, AI isn’t just a fascinating concept—it’s a rapidly evolving ecosystem. From advanced machine learning models to autonomous AI agents, and from generative tools to specialized AI subfields, new innovations emerge almost daily, transforming industries and reshaping the way we interact with technology.
Having said that, the topic remains as complex as ever. Which is exactly why we’re here to answer the question: how does Artificial Intelligence (AI) work?
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an interdisciplinary science focused on building machines able to complete tasks that typically require human intelligence.
Machines equipped with this technology are capable of learning from experience, processing data, and recognizing patterns, or even create completely new data as in the case of Generative AI technology.
Crucially, AI is able to perform those tasks without being explicitly instructed – its algorithms process data similarly to natural intelligence. Thus, AI systems can make reasonable decisions based on solid training data, as well as predict their far-reaching consequences.
What are the types of Artificial Intelligence?
Before we explain how Artificial Intelligence works, we need to underline the fact that there are different types of AI exploring various scopes of tasks and mechanisms. The technology itself has evolved significantly and can now be categorized into several broad groups:
- Narrow AI, also called “Weak AI”.
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), also called “General AI”.
- Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI), also called “Strong AI”.
Narrow Artificial Intelligence
This is the most recognized and widely used type of AI today. Narrow Artificial Intelligence (or Weak AI) is designed to perform specific tasks, such as analyzing images, processing human language, or recommending content. While these computer systems can be incredibly advanced, they operate within predefined boundaries and do not possess true understanding or independent thought.
Even if you haven’t heard the term before, you’ve almost certainly interacted with Narrow AI. Some common examples include:
- Large language models like GPT-4, Gemini, and Claude
- Virtual assistants like Alexa and Siri
- Search engines and recommendation algorithms
- AI-powered customer support chatbots
With AI agents becoming increasingly sophisticated, Narrow AI is evolving into more autonomous systems that can carry out complex workflows with minimal human supervision.
Artificial General Intelligence
AGI represents the next frontier of AI development. Unlike Narrow AI, AGI is designed to think, learn, and adapt in a way that mimics human cognition. It should be able to generalize knowledge across different fields, solve problems independently, and improve its own capabilities without explicit programming.
Although AGI remains theoretical, recent advancements in self-learning AI models suggest that we may be closer than ever to achieving it. Some researchers believe we’ll see early forms of AGI within the next decade, while others argue that fundamental breakthroughs are still needed.
Artificial Super Intelligence
While many believe that we may be able to create AGI at some point in the future, Artificial Super Intelligence is considered a work of fiction for the most part.
ASI is supposed to be the most advanced type of AI, which not only imitates human intelligence but is also able to perform self-awareness. It equips machines with emotions, beliefs, and desires typical for humans. Crucially, self aware AI not only catches up to but also surpasses human abilities.
Now that we know the main types of AI, let’s get to the gist of it!
How does AI work?
Artificial Intelligence is built upon a wide range of disciplines that humanity has been refining for centuries. In 2025, modern AI continues to draw inspiration from philosophy, economics, medicine, mathematics, psychology, and neuroscience – while also incorporating breakthroughs in computational sciences, cognitive modeling, and ethics.
Explaining how Artificial Intelligence development works is fairly simple: it relies on vast datasets and advanced models to enable machines to learn, adapt, and perform tasks based on acquired knowledge. However, today’s AI goes beyond traditional pattern recognition – it can generate content, make autonomous decisions, and even collaborate with humans in creative and strategic processes.
Building a set of algorithms that ensures AI’s performance is a highly complex process. It involves not just reverse-engineering human capabilities, behaviors, and traits but also developing self-learning architectures that evolve and improve over time.
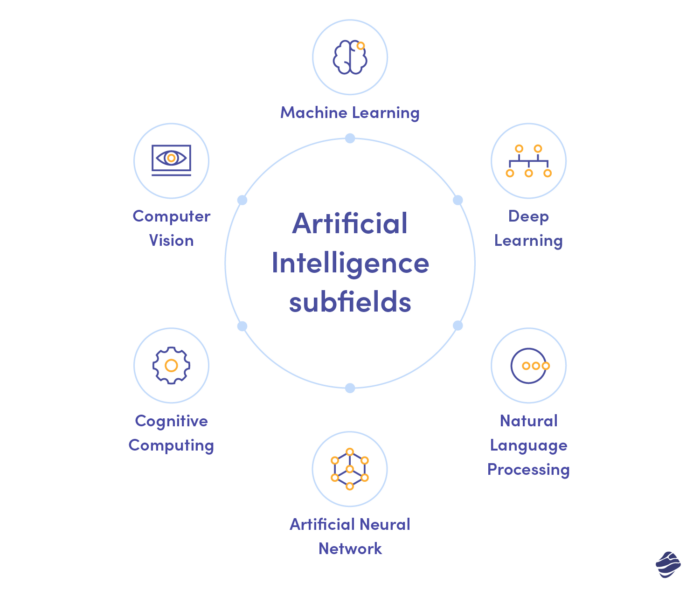
But to fully grasp how it’s all done, it’s essential to understand that Artificial Intelligence is based on a few subdomains that can be applied to a number of projects, and its careful combination results in intelligently behaving machines. Having said that, let us go through the most important AI subfields and see what they’re made of.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning solutions remain the backbone of AI development. The core idea behind ML is teaching a machine to make decisions based on past experience, structured and semi-structured input. It deals with analyzing data, recognizing patterns, and generating meaningful outputs.
Machine Learning is widely used in industries where automation and optimization are key, from financial forecasting and fraud detection to personalized recommendations and predictive maintenance. The latest ML models are now capable of self-improvement, allowing them to refine their decision-making over time without human intervention.
Deep Learning
Often mistaken for ML, Deep Learning is actually a specialized subset of Machine Learning that relies on deep neural networks – highly complex, layered algorithms designed to process vast amounts of data. DL excels at handling images, videos, text, and sound, making it the go-to approach for cutting-edge AI applications, including autonomous vehicles, real-time language translation, and content generation.
One of DL’s most exciting advancements is its ability to perform multimodal learning where a model can understand and generate content across multiple data types simultaneously, such as interpreting an image and describing it in natural language.
Curious? Check out our detailed Deep Learning vs Machine Learning comparison and discover their key differences!
Generative AI
Generative AI is one of the biggest AI trends in 2025. Unlike traditional ML, which focuses on predictions and classifications, Generative AI creates new content – whether it’s text, images, music, or even video. Powered by advanced deep learning models like transformers and diffusion networks, it enables machines to generate human-like responses, design artworks, write code, and even produce lifelike simulations.
Some of the most well-known applications of Generative AI include:
- AI-powered writing assistants and content generators
- Image and video creation tools (e.g., AI-generated artwork, deepfake technology)
- Music composition and sound design
- Code generation and AI-assisted programming
Natural Language Processing
NLP enables AI to understand, interpret, and generate human language, both in written and spoken form. In 2025, NLP has evolved significantly, allowing AI-powered chatbots, virtual assistants, and translation models to engage in more natural and context-aware conversations than ever before.
With the latest advancements in large language models (LLMs), AI is now capable of reasoning, summarizing, and generating high-quality content. NLP also plays a key role in real-time voice transcription, AI-powered journalism, legal document automation, and sentiment analysis, revolutionizing the processing and understanding of text-based information.
Computer Vision
Computer science is AI technology is dedicated to studying visual objects. Combined with Deep Learning techniques, Computer Vision software is capable of interpreting the content of images and videos. With computer vision, we can, for example, authenticate the person who wants to use our services, classify objects found in pictures and search content by images.
Modern Computer Vision applications include:
- Facial recognition for security and authentication
- Self driving cars that recognize road signs, obstacles, and pedestrians
- Medical imaging that detects anomalies in X-rays and MRIs
- Retail AI that enables cashier-less stores and smart inventory tracking
Artificial Neural Network
Neural networks form the foundation of Deep Learning. Inspired by the structure of the human brain, these layered algorithms process and analyze data in ways that mimic neural activity, enabling AI to recognize patterns, make predictions, and refine its own learning.
In 2025, neural networks are more efficient, scalable, and capable of adapting to new tasks than ever before. The rise of transformer-based architectures (such as those behind modern LLMs) has further pushed the boundaries of AI, allowing it to tackle tasks ranging from real-time speech recognition to protein folding simulations in medical research.
Cognitive Computing
Cognitive Computing aims to replicate human thought processes, allowing AI to analyze vast amounts of data and make decisions based on reasoning rather than predefined patterns. These AI models learn from experience, adapting to new scenarios dynamically. Cognitive AI is now widely used in:
- Healthcare – Assisting doctors with diagnoses and treatment recommendations
- Finance – Predicting market trends and managing risk in real time
- Enterprise AI – Acting as digital advisors in business strategy and customer support
With the integration of explainable AI (XAI) principles, Cognitive Computing is becoming more transparent, helping users understand how AI reaches its conclusions.
How to choose the right Artificial Intelligence solutions
To successfully decide what kind of AI technology is the best fit for your project, it’s crucial to carefully analyze your business needs, the desired features of the product, and the technological assets at your disposal.
Want to learn more about AI solutions, and see which ones are best suited for your business needs?