Imagine buying a car and just days later receiving a personalized video highlighting every aspect of your new purchase – its model, year, color, and even a look at the dealership where you got it. That’s what over 1.5 million Carvana customers experienced, thanks to generative AI.
What would have taken months of manual work was completed in a fraction of the time, showcasing the incredible power of AI to deliver personalized experiences on a massive scale. This trend is now sweeping through media and entertainment, revolutionizing how content is created and consumed.
But generative AI in media and entertainment is driving much more than just personalization. Companies are using artificial intelligence to develop AI-generated characters that interact with users in apps, create custom marketing campaigns that boost engagement, and streamline the entire production process. The technology is making content creation faster, more efficient, and more creative.
In this article, we’ll explore the top applications of generative AI in media and entertainment. We’ll look at standout generative AI solutions from leading companies, trends in media and entertainment, delve into the technology’s key benefits – such as increased efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced consumer engagement – and address the ethical considerations of using AI for creative tasks.
Key takeaways:
- AI tools streamline the production process, making content creation faster and more efficient, reducing costs, and increasing productivity.
- While AI doesn’t replace human creativity, it acts as a powerful tool that enhances and democratizes the creative process, allowing for more experimentation and innovation.
- The use of generative AI raises ethical concerns, including AI bias, content diversity, and the potential for misuse in creating deepfakes or personalized fraud.
- The ongoing development of AI technologies like RAG architecture and personalized AI solutions promises to further integrate AI into creative fields, balancing efficiency with originality and authenticity.
How does Generative AI in media and entertainment industry work?
At its core, generative artificial intelligence uses machine learning to spot patterns in large data sets. It doesn’t “understand” the world as we do, but it can create new content based on what it has learned. By pulling elements from its training data, AI can generate content from user prompts or video footage. However, it’s important to remember that AI doesn’t come up with truly original ideas – it reshapes existing ones.
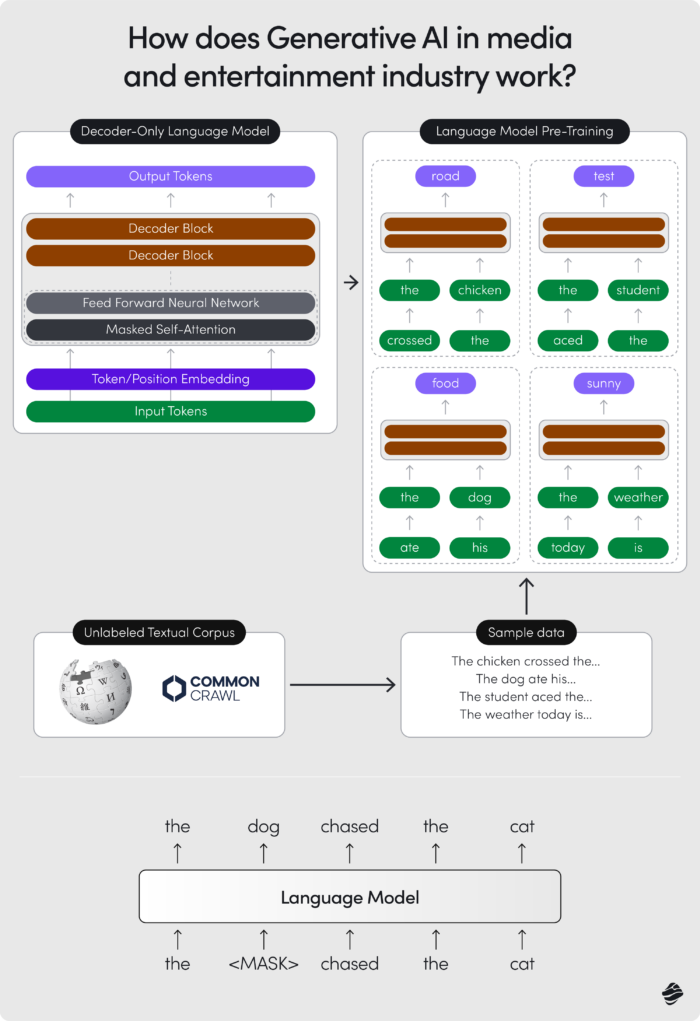
Some experts, like Meta’s Chief AI Scientist Yann LeCun, argue that this technology is not on track to reach Artificial General Intelligence – the kind of intelligence that could think and adapt like a human. But even with its current limitations, AI tools are advancing fast and constantly breaking new ground.
So, is AI truly creative and can be securely used in entertainment app and content development? It’s a complex question. While AI doesn’t have the same creativity as humans, it’s highly effective at quickly producing content tailored to specific needs.
According to a McKinsey report from May 2023, AI is widely used in marketing, sales, product development, and IT services. Marketing, in particular, has seen a huge surge in generative AI business use cases, as companies are tapping into its power to enhance creativity and efficiency.
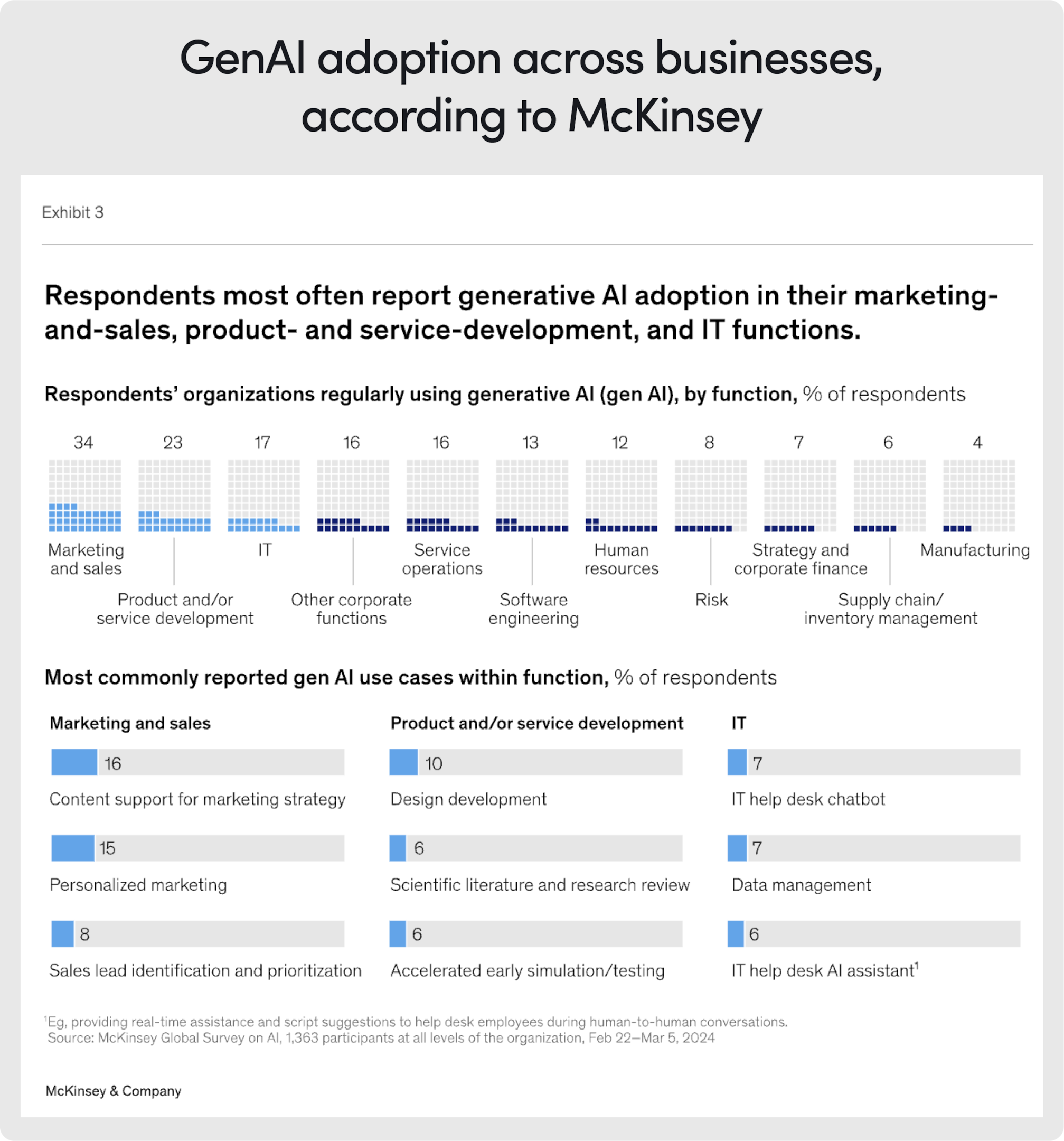
Since marketing, a highly creative industry, is so eager to embrace generative AI, there must be some significant benefits associated with it.
Let’s discuss what those benefits are.
Generative AI for content creation
Generative AI use cases in media and entertainment became a major topic in 2023, sparking debates about its impact on creative industries. As it began influencing Hollywood and other sectors, questions arose about whether AI would enhance or undermine human creativity. This tension culminated in events like the Writers Guild of America strike, where a key concern was AI’s potential to replace or devalue the work of writers and other creatives.
Media and entertainment companies are leveraging AI technology to enhance content creation and optimize consumer engagement.
Fast forward to 2024, and generative AI continues to reshape how content is created across media and entertainment. With even greater capabilities in mimicking human writing, design, and speech, AI is streamlining the creative process, allowing creators to work faster and more efficiently. From automating routine tasks to unlocking new creative possibilities, top generative AI projects are helping writers, marketers game developers, and designers do more with less effort.
Let’s explore how this technology is transforming everything from scriptwriting to visual effects, and how forward-thinking companies are leveraging AI to stay competitive.

Scriptwriting and storyboarding
In film and media, entertainment companies are leveraging generative AI to enhance scriptwriting and storyboarding processes. AI tools like ChatGPT, Gemini or Claude can generate entire scripts or dialogue, analyze existing stories to offer plot suggestions, and even create new characters and story arcs. This speeds up the writing process, helping writers get past creative blocks and develop new ideas.
When it comes to storyboarding, Generative AI can turn simple text prompts into detailed visual representations of scenes, giving filmmakers a clear picture of the story outlines how things will unfold. By streamlining these early production stages, AI allows filmmakers to focus on refining their vision and making creative adjustments long before the cameras start rolling.
Music composition and sound design
Generative AI is also making waves in music and sound design. Media and entertainment firms are leveraging generative AI for music composition and sound design, using tools that can analyze existing music to generate original scores, suggest harmonies, and even help with sound effects. This gives composers more freedom to experiment and refine their work while saving time on repetitive tasks.
Neal Mohan, CEO of YouTube, shares this optimistic view, calling AI a “revolution” that will help to “democratize” the creative process. He sees AI not as a replacement for human creativity, but as a powerful tool to boost it. “Our mantra at YouTube is that AI should not be a replacement for human creativity. It should be a tool used to enhance all of our creativity,” Mohan said.
In August 2023, YouTube took a significant step in this direction by launching its AI Music Incubator, a collaboration with Google DeepMind. This initiative allows artists to experiment with new AI tools, providing prompts to create unique sounds. According to Mohan, artists have expressed their excitement, saying, “It’s like a supercharger for their creativity,” enabling them to make music they wouldn’t have thought possible just a week earlier.
Automating content creation and personalization
One of the biggest benefits of generative AI for media companies in media and entertainment is its ability to automate content creation and personalization. Tools like Jasper AI can generate blog posts, articles, or social media content quickly, allowing creators to focus on fine-tuning instead of starting from scratch. This is a huge advantage in industries like marketing, where speed and volume are critical.
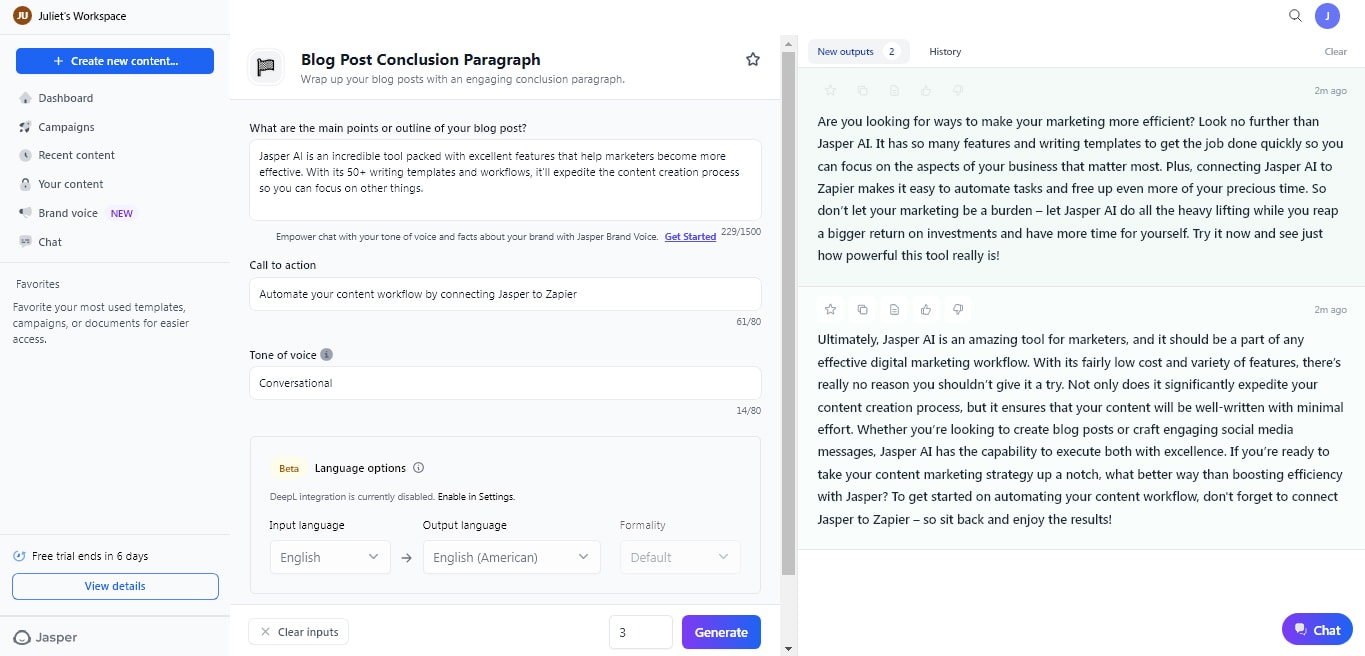
Optimizing Content for SEO
Generative AI is also a valuable tool for optimizing content for search engines. AI can suggest keywords, improve readability, and even generate meta tags that boost SEO rankings. This means creators don’t have to choose between quality and visibility – they can produce high-quality content that also performs well online.
Generative AI use cases in media and entertainment for content creation
Many companies are already using generative AI to revolutionize their content creation processes. Generative AI is also transforming the global media landscape by facilitating real-time natural language processing and translation and enhancing accessibility to diverse audiences:
- Jukin Media uses AI to sift through hours of video content, identifying the best moments for dynamic ad campaigns. This AI-driven approach helps brands create ads that resonate emotionally with viewers.
- L’Oréal teamed up with WPP and NVIDIA to create CREAITECH, a platform that allows influencers, marketers, and even consumers to co-create content. This AI-driven approach significantly reduces costs while empowering users to produce high-quality, personalized campaigns.

Personalization and user engagement
Generative AI in media and the entertainment business is not only transforming content creation but is also revolutionizing the way content is personalized and delivered in the media industry.
By leveraging data-driven insights, AI enables companies to tailor experiences to individual consumer preferences, moving away from one-size-fits-all approaches. This level of personalization creates more meaningful interactions between audiences and brands, driving higher engagement and loyalty.
Transforming user engagement through personalization
AI empowers consumers to take an active role in content creation. Whether it’s allowing users to step into the shoes of a photographer, designer, or writer, generative AI opens up new ways for people to interact with brands.
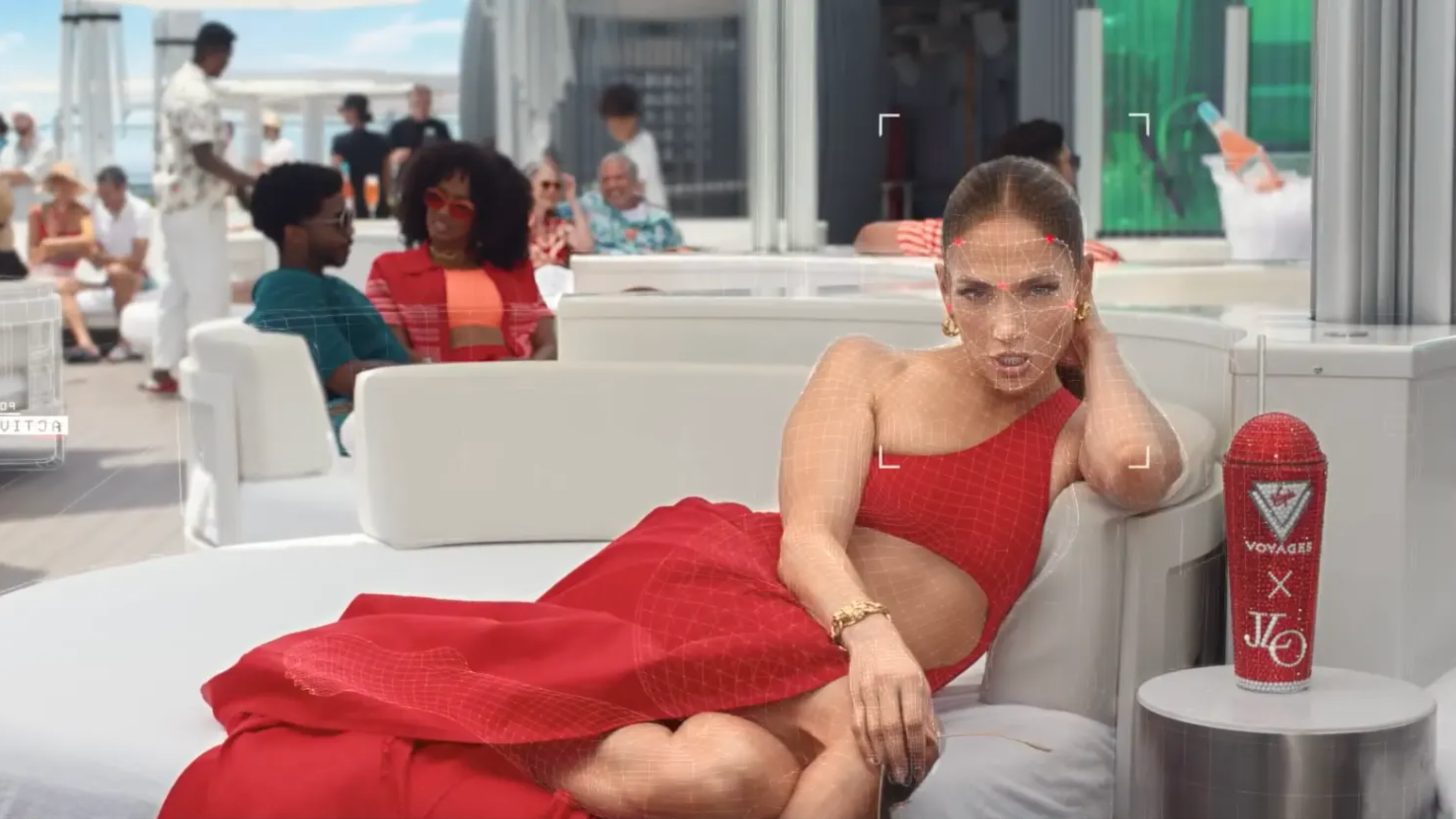

One standout example is Virgin Voyages’ Jen A.I. campaign, where users could generate personalized cruise invitations for loved ones, delivered by a virtual AI version of Jennifer Lopez. This campaign saw a 150% increase in engagement compared to traditional campaigns, showing the effectiveness of personalized AI-driven content.
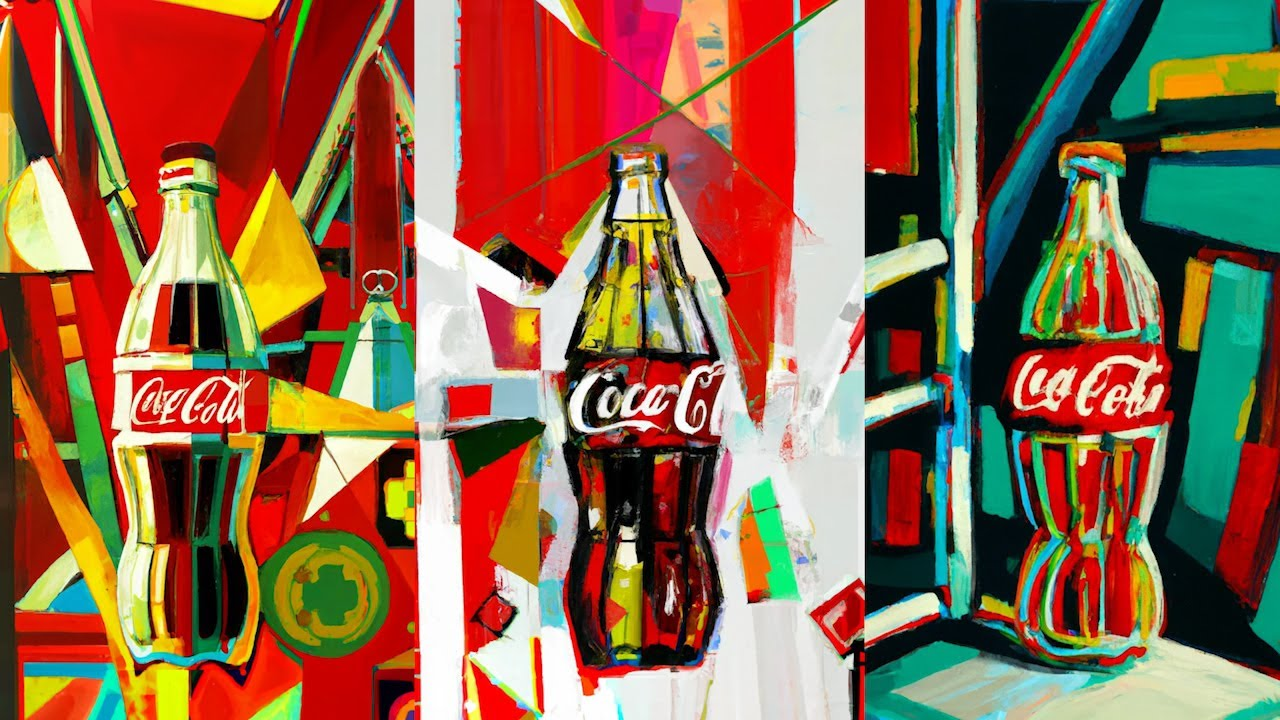

Similarly, Coca-Cola’s “Create Real Magic” campaign used the AI tool DALL-E to let users design unique artwork tied to the Coca-Cola brand. The best creations were displayed on billboards in iconic locations like Times Square and Piccadilly Circus, and top creators were invited to exclusive workshops with Coca-Cola and OpenAI teams. This deep level of interaction, where fans actively shape the brand’s narrative through their creative input, strengthens consumer-brand relationships and boosts purchase intent.
Greater efficiency at lower costs
Generative AI use cases in media and entertainment are dramatically increasing the efficiency of content production, allowing companies to generate more – whether it’s text, images, videos, or audio – much faster and at significantly lower costs.
Cost and time savings
The impact of generative AI on efficiency and cost reduction is clear.
A Boston Consulting Group study with 750 employees measured how AI influenced productivity. For tasks like generating product ideas, market segmentation, or drafting press releases, new employees saw a 30-40% increase in productivity, while more experienced employees improved by 20-30%. On average, employees completed 12% more tasks, all while maintaining high-quality output.
In the marketing world, the adoption of AI is equally transformative. In June, WPP, one of the world’s largest advertising agencies, launched an AI-powered production studio in collaboration with NVIDIA. This studio automates the creation of text, images, and videos that align with brand guidelines, ethical standards, and legal regulations. WPP’s CEO estimated that AI could reduce campaign production costs by up to 20%, simply by automating the content creation process.

Ethical considerations and challenges
Generative AI promises a utopia of faster, more abundant, and cost-effective content production. But utopia and dystopia are two sides of the same coin. While we gain much from AI, it’s worth asking – what might we be losing, especially in the media and entertainment sector, industries where ethical considerations and challenges are significant?
Virtually every beneficial application of generative AI can be misused. For instance, a personalized video thanking you for your car purchase is a delightful gesture from a brand.
But when AI floods your inbox with thousands of personalized sales emails, it feels like harassment. Worse, AI can personalize fraud attempts or create political deepfakes that manipulate public opinion, threatening our trust in media.
While extreme examples like deepfakes are being addressed by legal frameworks, many smaller risks are only beginning to be examined. So, what are the hidden dangers of using generative AI in media and entertainment?
Let’s dive deeper into the risks of generative AI in business.
The decline of content diversity
A significant concern is AI’s effect on content diversity. Generative AI is increasingly being used to create news articles, which can impact the diversity and originality of news content.
In a 2023 study by NYU, 38 authors wrote 300 essays – some using AI, some without. Surprisingly, the AI-assisted essays were strikingly similar in their choice of words, arguments, and reasoning. AI tends to prefer certain phrases spoken words and styles based on its training data, which could lead to a homogenization of language and ideas.
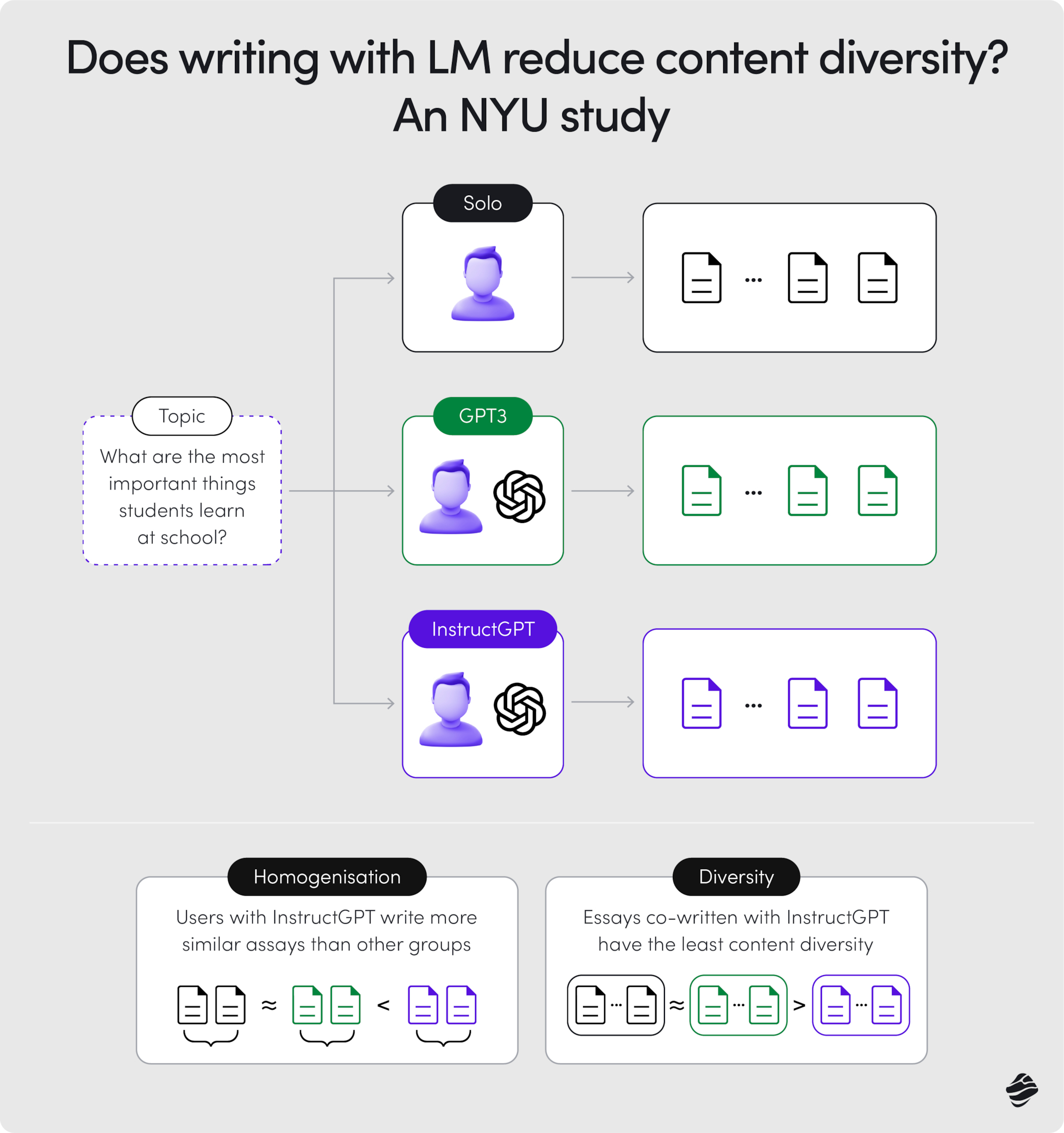
This issue is even more problematic when AI is used for research and innovation. While AI is excellent at spotting patterns in large data sets, its mostly linear thinking doesn’t always work in our complex world.
Human creativity thrives on non-linear, unconventional ideas, often pushing innovation forward. Generative AI, by nature, is less capable of such leaps.
Content overload and its consequences
We live in a world overflowing with information but lacking meaning – something philosopher Jean Baudrillard predicted over 45 years ago.
Today, the sheer volume of content we are exposed to makes it harder for audiences to focus. Our average attention span for a piece of content has shrunk to just 6 seconds, making it harder than ever to engage deeply with information.
This content overload doesn’t just hurt our ability to focus; it makes filtering important information more challenging. As a result, valuable insights often get lost in a sea of noise.
This overproduction of content is contributing to what Baudrillard called “hyperreality,” where the line between real and artificial blurs, making it harder to tell truth from fiction.
AI’s ability to replicate virtual reality more convincingly only deepens this challenge, potentially leading to isolation, disconnection, and difficulty distinguishing between human and AI-created content.
AI bias and ethical concerns
Another significant issue is AI bias, which stems from the data on which models are trained. AI learns from the patterns it sees in data, and those patterns can reflect societal biases and stereotypes.
For example, when a prompt like “Native American” is entered into some AI image generators, the results often depict stereotypical imagery of traditional headdresses, failing to capture the diversity of modern Native American life.

Efforts to reduce AI bias are underway, but the solutions are imperfect. For instance, some AI models like DALL-E now aim to diversify results when generating images of people. If a user requests an image of a “software engineer” without specifying gender or race, the AI system ensures a mix of results.
But this method – adjusting the AI’s internal prompts – isn’t a foolproof solution and can lead to unnatural results, like forcing diversity in ways that don’t always make sense.
A better approach can be seen in Amazon’s CONSIDERS framework, which calls for a multidisciplinary evaluation of AI results, considering usability, aesthetics, and cognitive biases.
Additionally, tools like guardrails and evaluators are being developed to ensure AI applications, like customer service chatbots, don’t return unethical or inappropriate responses.
The threat of model collapse
Model collapse is another emerging concern. This occurs when AI models are trained using data generated by other AI models rather than human-created data. Over time, these models lose the ability to create diverse, meaningful responses to novel data, instead generating repetitive or nonsensical content.
Human-generated data is crucial because it reflects the full richness of human experience, cultural diversity, and linguistic complexity.
When AI begins to rely too heavily on AI-generated data, it loses this richness, leading to a decline in quality. In the long term, this could result in less creative, less innovative AI outputs, further entrenching homogenization.
What’s next for Generative AI in media and entertainment
While there are undeniable risks in using AI, we shouldn’t let them overshadow the opportunities. The key is to be aware of the potential risks of generative AI in business. By approaching it responsibly, we can enjoy the benefits without sacrificing originality and authenticity.
How to use AI wisely?
First and foremost, we need to treat AI as a tool, not a “magic wand.” Understanding how it works – how it generates content and what data it relies on – shifts our perspective. When we stop seeing AI as a magical solution, we make clearer decisions. We stay focused on our business, marketing, or sales goals, using AI as a support, not a replacement.
Leverage advanced AI techniques
Once we grasp how popular AI tools like Gemini, Claude, or ChatGPT work, we often realize they may not fully meet our business needs. In such cases, building more personalized AI solutions could be the next step.
These customized solutions can integrate with your website or app, using your specific data to generate responses. This means that AI tools can reference the most relevant and accurate information rather than relying solely on the data in its model. Personalizing AI tools is becoming easier, thanks to companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google, which are increasingly offering ways to adapt their models to unique business needs.
Another option is creating a custom AI solution based on natural language and models that incorporate your data. These systems can safely and effectively generate high-quality content while minimizing issues like “AI hallucinations” (incorrect or nonsensical outputs). Contrary to popular belief, building these solutions doesn’t have to be expensive or time-consuming.
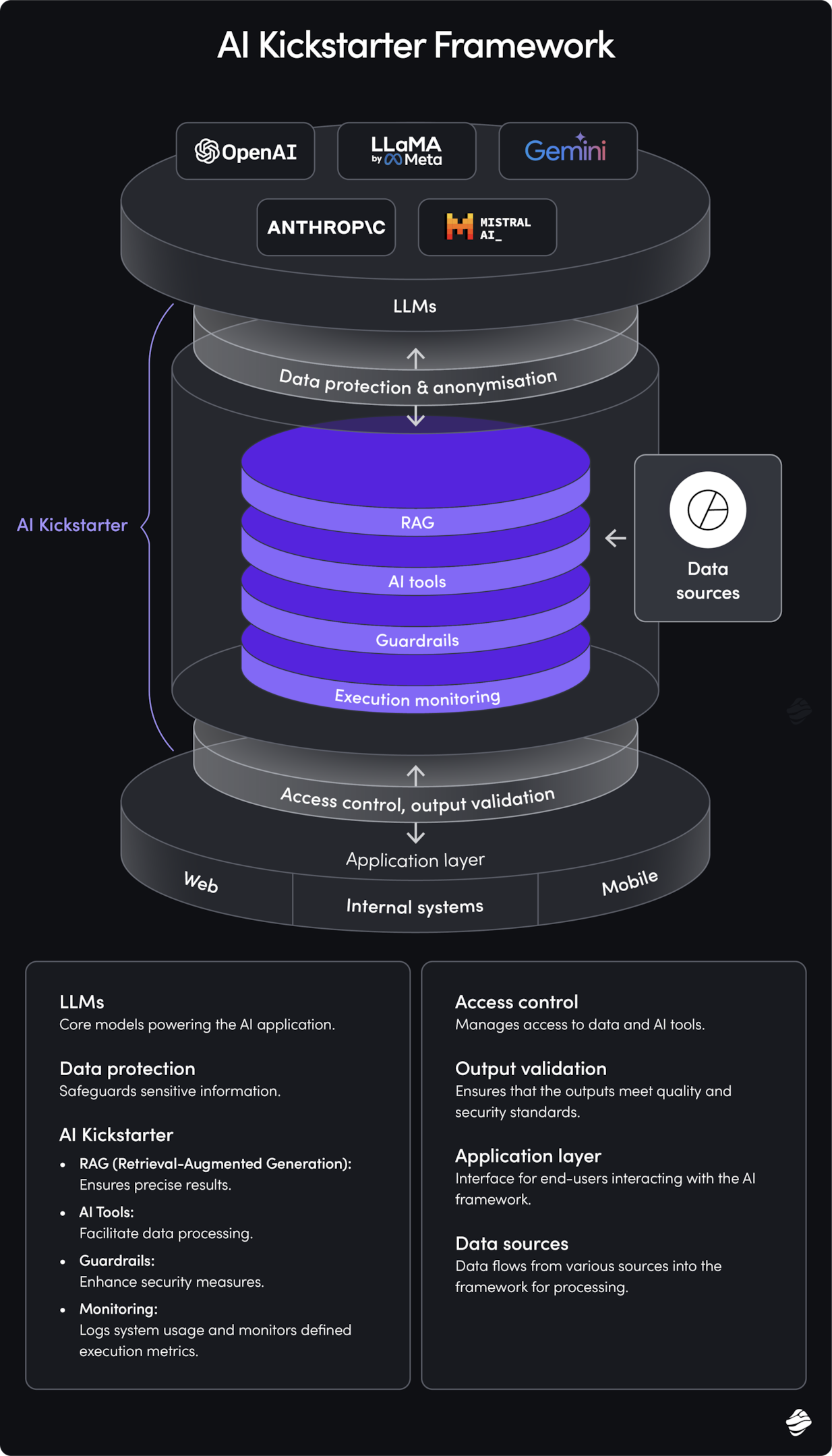
At Miquido, we’ve developed a framework called AI Kickstarter, which helps businesses quickly build personalized AI applications that are both safe and ethical. One of the key elements is the RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) architecture, which allows AI models to retrieve relevant information from your data before generating responses.
This ensures that the AI produces high-quality, context-aware content based on the right sources.
Stay within the legal framework
Using AI doesn’t free us from copyright laws. When creating content with AI, we need to remember not to process someone else’s data or plagiarize written material without permission. Moreover, it’s essential to stay aware of new regulations like the AI Act in the European Union, which requires AI-generated content to be clearly labeled.
Don’t neglect your own creativity
AI should support your creative processes, not replace them. And it’s not just because AI-generated content currently lacks true creativity or high quality – this argument may become irrelevant as AI improves in the coming years.
More importantly, the process of creation itself is valuable. It helps us discover new things about ourselves, explore fresh ideas, and grow.
Creativity is more than just the result; it’s the journey that makes us better thinkers, innovators, and creators.
By using AI responsibly and strategically, we can harness its power to enhance our work while ensuring that we stay in control of the creative process.
The future of AI in business isn’t about choosing between technology and human ingenuity – it’s about blending the two to achieve something greater.





![[header] top ai use cases in manufacturing](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/header-top-ai-use-cases-in-manufacturing-432x288.jpg)


![[header] how is ai used in the music industry overcoming trust, fraud & transparency challenges with ai](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/header-how-is-ai-used-in-the-music-industry_-overcoming-trust-fraud-transparency-challenges-with-ai-432x288.jpg)