Generative AI is defined as deep learning models that can create high-quality texts, images, and other content based on the data they were trained on.
Gen AI presents a lot of advantages in the digital space. One notable example is the inclusion of AI features in mobile apps to make them more engaging.
In cybersecurity, generative AI can analyse data, identify threats, and recommend solutions for preventing malicious attacks. In this blog post, we’ll go deeper into how Gen AI can help fortify cybersecurity measures.
Benefits of Gen AI in Cybersecurity
Using generative AI in business comes with a lot of potential. For cybersecurity, Gen AI comes with remarkable benefits such as:
1. Improved Threat Detection
Generative AI can seamlessly observe and learn patterns in a vast data range, making it possible for cybersecurity professionals to continuously identify and understand cybersecurity threats.
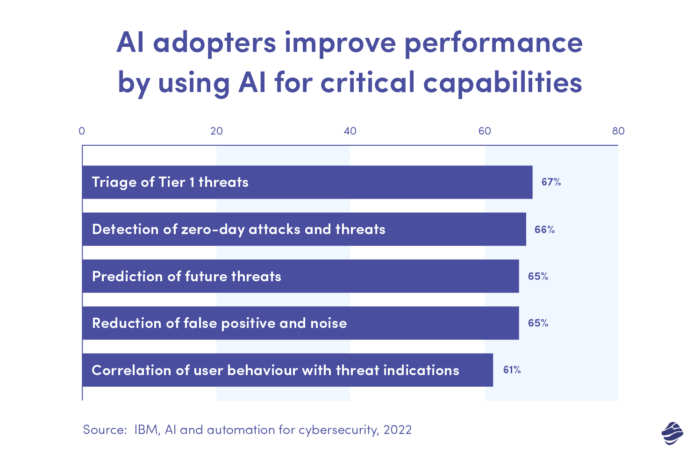
In research by IBM, 66% of AI adopters revealed that Generative AI has helped them predict zero-day attacks and threats. Zero-day attacks refer to newer threats that traditional systems may miss.
Another 65% said Gen AI helps with the correlation of user behaviour to detect threats.
With Gen AI in cybersecurity, it’ll be much easier to identify slight behavioural variations that may indicate a potential attack. For instance, Gen AI can automatically analyse new files and code to detect suspicious behaviour. Or analyse email content, language patterns, and sender information to identify fake emails accurately.
2. Predictive Analytics
Gen AI can make accurate predictions of future outcomes based on an analysis of repetitive patterns in large data sets like security logs, network traffic, threat intelligence, and so on.
For example, Gen AI can analyse patterns from previous vulnerabilities or attacks and use that to predict possible threats that may come up in the future. That allows organisations and security teams to implement measures to prevent such attacks.
3. Automated Responses
Based on previously observed patterns and attacks, Gen AI can generate automated responses for different types of threats. For instance, you can trigger actions that block malicious IP addresses, adjust firewall rules against intrusion attempts, or prevent malware from spreading.
Using generative AI in cybersecurity, you can also generate automated responses for patching security vulnerabilities before an attack or redirecting suspicious traffic to honeypots for further investigation.
Additionally, Gen AI can automatically generate detailed reports after analysing your security logs.
3 Major Challenges & Risks of Using Generative AI in Cybersecurity
Apart from the benefits, there are potential risks and challenges associated with using Gen AI for cybersecurity. These include:
1. Data Privacy Concerns
Training Generative AI models or analysing existing data usually means that you’d provide AI tools with a lot of information from your organisation. It’s how you can get more accurate results.
However, there’s a concern about how your data privacy is protected. For instance, there’s a likelihood that personal information may be misused if left unchecked— especially where ethical guidelines and data governance practices are neglected.
Also, Gen AI models are only as good as the data they’re trained on. So, if biased data is used, there’s a possibility that the model might miss specific patterns and make inaccurate or biased predictions. In cybersecurity, this could mean overlooking particular types of attacks or underestimating certain threats.
2. AI Being Used Maliciously
Gen AI tools are becoming more accessible and affordable. As a result, it’s not only accessible to a legitimate generative AI development company but can also be used by individuals with malicious intentions.
For example, hackers can easily use generative AI to create malicious codes that target weak security protocols.
Additionally, generative AI can be used to create new and sophisticated attack methods, making it harder for traditional security measures to keep up.
For instance, Gen AI can create highly believable fake emails or websites, making it harder for users to identify and avoid scams. That means unsuspecting users could be lured into providing sensitive information or downloading harmful content.

3. Job Displacement
Efficiency is one of the biggest selling points of using generative AI in cybersecurity. This technology can analyse vast amounts of data faster than traditional cybersecurity techniques.
Unfortunately, this also means that AI can potentially displace so many jobs. In fact, a report by Goldman Sachs explains that AI will replace 300 million jobs through automation.
Cybersecurity experts handling repetitive tasks like threat detection and malware analysis will likely be the first to be affected by gen AI automation.
It’s not all gloom and doom, though. Human expertise will still be required. The best solution, especially for cybersecurity professionals, is to reskill or upskill. This is especially crucial for professionals handling entry-level tasks.
For starters, professionals will need to get comfortable working alongside AI. Secondly, more organisations will need human experts who can craft solid cybersecurity strategies, optimise AI systems, and oversee risk management.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies of Gen AI in Cybersecurity
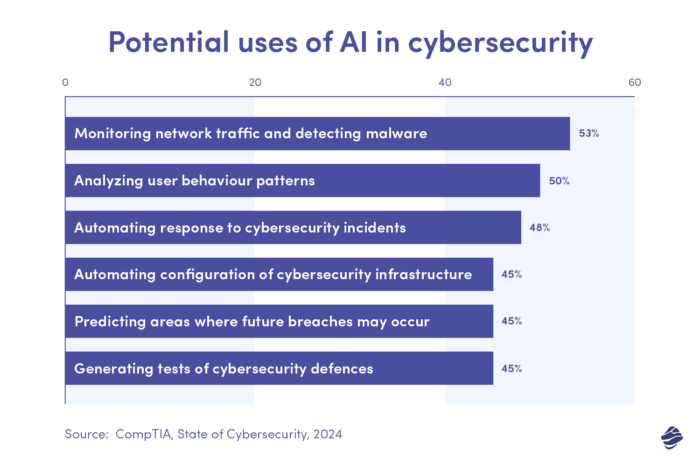
Before we go on, let’s briefly look at real-world examples and generative AI use cases in cybersecurity, where integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a crucial tool with immense potential. AI has numerous applications in cybersecurity that can help strengthen defences, improve threat detection, and increase the resilience of digital infrastructures against constantly evolving cyber threats. Let’s delve deeper into real-life examples to understand how it can be used to mitigate cyber risks.
Google is not just using generative AI to guard against cyber threats in its organisation. It also creates Generative AI solutions to help other organisations do the same.
Google has also announced the launch of cyber defence initiatives that help improve cybersecurity. One such initiative is SAIF – Secure AI Framework, which Google has used in its software development process.
SAIF is a conceptual framework that aims to protect AI systems against threats and attacks. It can be used to tackle risks like stealing a particular AI model, data poisoning through generative AI outputs, or malicious inputs through prompt injections. SAIF is also effective for monitoring inputs and outputs to detect threats and guard against attacks by automating defences.
Also, Google intends to release Magika, a cybersecurity tool for identifying file types to detect malware. Google has successfully used this tool to protect its products like Google Drive, Gmail, and Safe browsing.
PayPal
PayPal is an international payment platform that makes transactions easy for merchants and customers. To implement cybersecurity measures, PayPal trains advanced Machine Learning (ML) models to detect real-time fraudulent activity.
Typically, PayPal’s network provides a vast amount of transaction data that the AI can learn from. Results from the ML model can then be used to improve authentication systems and catch fraudulent activities. The model continues to learn and adapt as PayPal’s dataset grows.
ED&F Man Holdings
ED&F is a commodities trader that has successfully used Generative AI for threat detection. They achieved this using Cognito, an AI threat detection platform by Vectra.
ED&F provided detailed information about its network activity, including communication between devices, data transfers, and user actions. Cognito then uses this data to identify vulnerabilities and suspicious behaviour in real-time.
According to ED&F’s cybersecurity manager, Carmelo Gallo, Cognito played a key role in helping to identify risky employee behaviours like unauthorised remote access to data and files. ED&F also discovered a command-and-control malware that has lingered in their system for a long time.
Generative AI vs Traditional Cybersecurity Methods
Traditional cybersecurity methods thrive on a rule-based system and manual analysis.
Rule-based systems typically involve setting predefined instructions that tell the system what to watch for. This would usually be based on unique patterns exhibited by popular malware or security breaches.
When these rules flag suspicious activity, you typically must manually assess and resolve the vulnerabilities. Traditional cybersecurity methods also depend greatly on human intervention and constant updates.
Unlike traditional methods that struggle with large databases, Gen AI can assess a massive chunk of data, allowing it to detect complex patterns that a human analyst might miss. This also helps you understand vulnerabilities in more detail.
Beyond analysing data, generative AI can help to create solutions to potential threats— for instance, generating secure passwords or designing more efficient security protocols. So, it’s more proactive.
While AI proves to be a more effective tool for implementing stronger cybersecurity measures, human intervention will always be needed. So, you can leverage the strengths of both methods for better results.
For instance, you can use traditional methods to verify predictions made by AI and ensure better accuracy. You can also use AI recommendations to enhance the manual configurations that you set up.
7 Emerging Trends in AI and Cybersecurity:
Generative AI in cybersecurity is rapidly evolving. Here, we explore several emerging trends likely to shape the future.
- Prioritisation of AI Cloud and Security: We’re seeing an integration between AI systems and cloud infrastructure. This should facilitate real-time threat detection and prevention.
- Expansion of Gen AI-powered Cybersecurity Tools: Gen AI is going to be resourceful in creating fake systems or honeypots for deceiving cyber attackers. The tech’s ability to analyse vast amounts of data and identify patterns will also help create novel cybersecurity solutions.
- Emphasis on Cyber Resilience: AI’s ability to predict and patch vulnerabilities will see improved resilience of cybersecurity systems. The technology will help in fixing weaknesses before attackers can exploit them.
- Increasingly Sophisticated Cyber-Attacks Facilitated by Gen AI: Gen AI can facilitate cyber attacks at scale, something that was initially very challenging. Deep fakes are also getting really good, increasing the risk of social engineering through personalised phishing campaigns.
- Use of AI-Powered Automation Enabling Cybersecurity Teams To Drive Improved Insights: AI will eventually take over time-consuming tasks like log review as well as threat detection and analysis. This will allow human experts to focus on more strategic duties like decision-making and developing cybersecurity strategies.
Besides improving cybersecurity, this trend shows that the future requires collaboration between human experts and AI systems.
- Rise in Specialized Language Models: A recent publication by the World Economic Forum suggests that large language models have been quite effective in processing vast amounts of data.
However, this broad usage may not apply to specialised domains like cybersecurity. As a result, we’re likely to see a transition to smaller and more specialised language models, which can enable teams to access more precise and actionable insights.
- Focus on Proactive Threat Detection: We’re seeing Gen AI being used to enhance the security of mobile applications by focusing on proactive threat detection and real-time responses.
This is one of the growing AI trends in mobile apps. AI can observe user behaviour to detect oddities that may indicate a security breach. Some examples include unusual login attempts or other suspicious activity.
As we glance into the future of AI in cybersecurity, it’s safe to predict that there will be more advanced tools and platforms to target the ever-increasing threats that plague cyberspace.
How To Implement Gen AI in Cybersecurity
Integrating generative AI in your cybersecurity strategy is a remarkable step in the right direction. However, there’s a need for careful planning and implementation.
So, in this session, we’ll look at a few ways to implement Gen AI in cybersecurity effectively:
- Start Small
Instead of overhauling your existing security system, consider starting with the basics and scaling up with time.
So, you first want to identify use cases that are more valuable to your organisation. This could be to patch up vulnerabilities or improve your responses to attacks.
- Train Employees and Regulate AI Usage
Next, train your team on how to use Gen AI to detect issues and how to interpret outputs. Then, you can gradually adopt AI-based security tools for tasks like real-time threat detection and incident responses.
You also want to update your security policies and regulations to promote the usage of AI tools. For instance, show employees examples of what’s acceptable when using generative AI tools in your cybersecurity measures.
Due to the possibility of misusing AI tools and the security risks that may follow, it’s advisable to put measures in place to coordinate how Gen AI is used in your organisation. For example, you can limit usage to only tools vetted and approved by your IT department.
- Choose the Right AI Technology
There are various AI technologies you can use in your cybersecurity strategy. Some examples include:
Machine Learning (ML), which uses algorithms to learn from data and make predictions. It’s useful if you want to detect threats and predict vulnerabilities.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) – focuses on understanding and manipulating human language. Useful for security processes like analysing emails or security logs and automating incident responses.
Then, we have anomaly detection systems (ADS), which identify deviations from standard data patterns. ADS can detect network intrusions, unusual user behaviour, or malware activity.
Advisably, you want to use the technology that addresses specific security issues you’re targeting.
- Use High-Quality Data
Invest in collecting and preparing high-quality, unbiased data specific to your needs. Ideally, this should be data relevant to your use case and threat landscape. You also want to use diverse data variations to avoid bias in the output.
Consider using simulated data in place of any information that may be sensitive. Be sure to secure your data storage and access controls to protect sensitive information.
- Monitor and adapt
Finally, cyber threats are constantly evolving, so your GenAI implementation must also adapt. Regularly monitor its performance, update data and models, and address any emerging challenges.
You can also partner with a company that provides generative AI services for a more efficient implementation.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
The growing use of Gen AI presents a need for regulations to be implemented, especially as it concerns ethical adoption and risk revelation. Ideally, the use of AI tools should be within the guidelines established by existing regulatory bodies.
Laws like the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) have set the standards for user privacy and data protection with AI cybersecurity models. Some of these include:
- Collect and use only data that are necessary for specific and legitimate purposes.
- Implement effective measures to safeguard user data.
- Provide information that helps users understand how the AI platforms work.
One study also highlights well-known frameworks that guide the ethical adoption of AI. They include fairness, transparency, accountability, and robustness.
Fairness – this involves ensuring that the AI technology is fair and unbiased— especially with the data the AI is trained with. This involves taking measures to prevent any form of discrimination based on factors like gender, age, or socioeconomic status.
Transparency and accountability demand that AI platform vendors be truthful about how the AI systems work. They also need to be accountable for errors or problems encountered using these AI solutions. Users must understand how their data is used or stored.
Robustness highlights the need to build AI systems that are reliable, secure, and resilient to error.
There’s also the Human-centered design, which promotes building AI systems with human needs in mind instead of focusing on a technicality.
Expert Opinions and Forecasts on Using Gen AI for Cybersecurity
So, what are the cybersecurity experts saying about generative AI in cybersecurity?
Kunle Fadeyi, a member of the Forbes Technology Council, agrees that AI is revolutionising cybersecurity by providing proactive security measures that can help protect against cyberattacks. He calls this “security by design,” which typically involves identifying and closing security gaps that cybercriminals may try to exploit.
Mike Lieberman, CTO and co-founder of Kusari, also predicts that AI will help companies address cybersecurity by allowing them to detect bad security patterns in a given code or configuration. According to Lieberman, AI will provide guidance in more complex security scenarios. However, AI tools should only be used as signals, not decision-makers.
Finally, cyber security expert and CEO of Logpoint, Jesper Zerlang, recommends that organisations infuse cybersecurity strategies into the overall business objectives. This is because the risk of cyber attacks will likely increase as businesses rely on digital processes.
Blending cybersecurity into business objectives will ensure organisations can proactively protect valuable business assets and build the confidence of stakeholders.
In Closing: How To Use Gen AI for Cybersecurity
As technology evolves, threats and potential attacks also continue to saturate the digital space. This results in the need for more advanced approaches for identifying and safeguarding businesses and users from malicious cyber activities. That brings us to the need to complement traditional security measures with generative AI methods.
Today, we saw how Gen AI provides a faster and more efficient way to identify threats, predict security issues, and automate incident responses. We also looked into effective ways to implement Gen AI in your cybersecurity measures. They include identifying specific use cases, choosing the right technology, training your employees, and continuously monitoring your security measures.
You should also take note of the ethical considerations in using gen AI for cybersecurity and emerging AI cybersecurity trends.
Overall, we hope this guide has shown you how artificial intelligence can help improve your security posture. Use these insights to implement a robust cybersecurity framework for your organisation.