As embedded finance features becomes more widespread, companies are finding new payment capabilities to integrate financial transactions seamlessly.
What is embedded finance? In a nutshell, means letting your customers access financial services directly on your platform and in context. This modern functionality cuts out the extra steps and makes life easier for consumers and your business.
It can be helpful to examine some embedded finance examples to see how it’s currently being used, where there’s room for improvement, and what opportunities lie ahead. Just like gamification in fintech, embedded finance is bringing significant value to companies, fueling profit and growth.
Dive in and check how it is shaping customer habits and creating new opportunities.
Embedded finance overview
Before the development of embedded finance or banking, making a purchase often meant multiple steps: finding a product, getting redirected to a payment gateway, applying for financing through a third-party lender, or searching for insurance separately. Each step added friction, making transactions slower and more complicated.
With embedded finance, the third-party bank or lender disappears. Businesses no longer have to send customers elsewhere for financial services. Instead, embedded finance companies act as a bridge, closing the gap between businesses and consumers.
At its core, embedded finance means integrating financial tools directly into non-financial platforms. Popular embedded financial services include:
- Payments
- Lending
- Insurance
- Investments
- Digital wallets
- Subscription management
- Bill payments
- Identity verification
- Currency exchange
- Tax services
Instead of going to a financial institution or a separate banking app, users can access payments and other financial services where they already shop, book, or interact.
The embedded finance trend makes transactions faster, more convenient, and more accessible. Chances are, you’ve already used embedded finance without realizing it. This might have happened while hailing a ride, shopping online, or booking a trip.
For business owners, embedded finance is an opportunity to boost revenue, increase customer loyalty, and simplify the buying process. With 70% of business leaders increasing investments in personalization, enhancing customer experience has become a priority.
Adopting embedded finance means creating smoother user experiences while unlocking new revenue streams without relying on financial service providers.
Now, let’s explore some real-world embedded finance use cases across different industries.
Embedded payments
Embedded payment technology integrates payment processing directly into a platform’s foundational code through APIs and software development kits (SDKs). It allows transactions to happen within the platform’s interface instead of redirecting users to an external payment gateway.
Customers can enter their card details or pay via alternative methods like QR codes or bank transfers without ever leaving the website or app.
One of the earliest examples of embedded payments was Amazon’s introduction of “1-Click” purchasing in 1999. This feature allowed customers to make purchases with a single click, making checkout faster and more convenient. It eliminated the need to re-enter payment information for every transaction.

Amazon even patented this technology and later licensed it to other companies.
Embedded payment services reduce friction, speed up checkout, and improve overall customer engagement. Businesses that integrate embedded payments increase conversion rates, reduce cart abandonment, and enhance user satisfaction.
Here are some common embedded finance examples in payments.
Ride-sharing apps
Apps like Uber, Lyft, and Bolt have changed how we pay for transportation. Instead of handling cash or pulling out a debit or credit card to pay after every ride, payments happen automatically in the background.
When a user requests a ride, the app accesses their stored payment method, like bank account payment. After the trip, the system instantly charges the fare and sends a receipt via email or in-app notifications.
Embedded payments remove the hassle of manual transactions, thus making the experience smoother for riders and drivers.
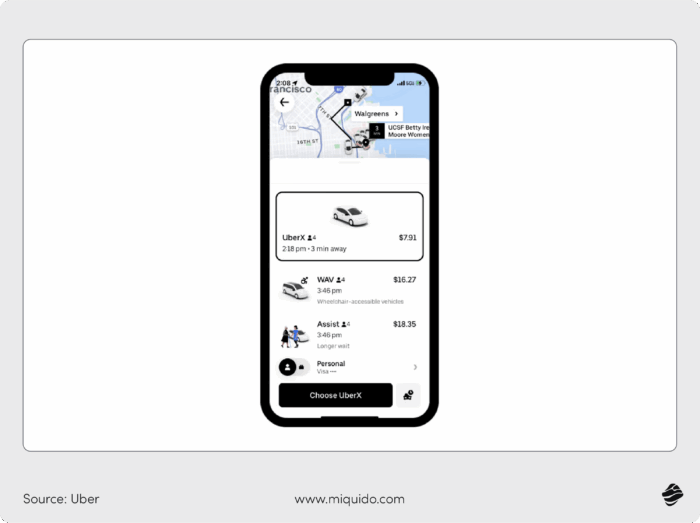
For transport businesses, streamlined payments mean:
- Faster transactions
- Better cash flow for drivers
- Increased customer retention
The ease of use encourages more people to use these services, knowing they won’t have to worry about payment at the end of a trip.
Additionally, this embedded finance example solved a major problem–passengers skipping payments.
Before this, taxi drivers often had to chase after riders who left without paying.
With payments handled automatically through the app, every ride is charged the moment it ends, eliminating the risk of unpaid fares and ensuring drivers get paid without hassle.
E-commerce platforms
Online shopping is faster and more seamless thanks to embedded payments on platforms like Amazon, Etsy, and Shopify stores.
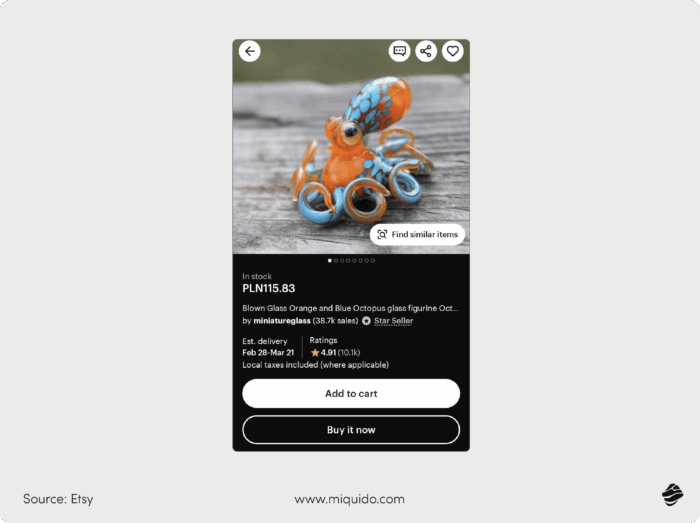
These e-commerce platforms allow customers to store payment details, use one-click checkout, or pay via other payment methods. They simply become a one-stop shop for all their needs.
In the checkout process, embedded payments functionality reduces checkout steps, which lowers cart abandonment rates significantly. The buying process is also faster and more secure since customers don’t have to enter card details for every purchase manually.
For brands, offering an integrated payment system leads to higher conversions and better customer trust.
Some platforms take it a step further by offering their own payment processing solutions. For example, Shopify provides Shopify Payments, which allows merchants to handle transactions directly without depending on third-party providers.
Embedded lending
Embedded lending makes borrowing more accessible, seamless, and convenient. It increases purchasing power, reduces friction at checkout, and helps retailers boost sales through flexible payment terms.
Embedded lending allows consumers to access credit directly within the platforms they already use. It simply removes the need to apply for a loan through a bank.
This technology relies on APIs and algorithms to assess creditworthiness in real time to enable instant financing decisions. Customers can split purchases into installments or finance high-ticket items without leaving the platform.
When a user selects a financing option, the platform communicates with an embedded lending provider through an API. This retrieves financial data, evaluates risk, and approves or declines the loan within seconds.
Some systems use alternative credit scoring models that analyze transaction history or spending patterns. This expands access to credit beyond traditional banking requirements.
Here are two key embedded finance examples in lending.
Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services
Services like Klarna, Afterpay, and Affirm let shoppers split payments into smaller, interest-free installments instead of paying the full amount upfront.
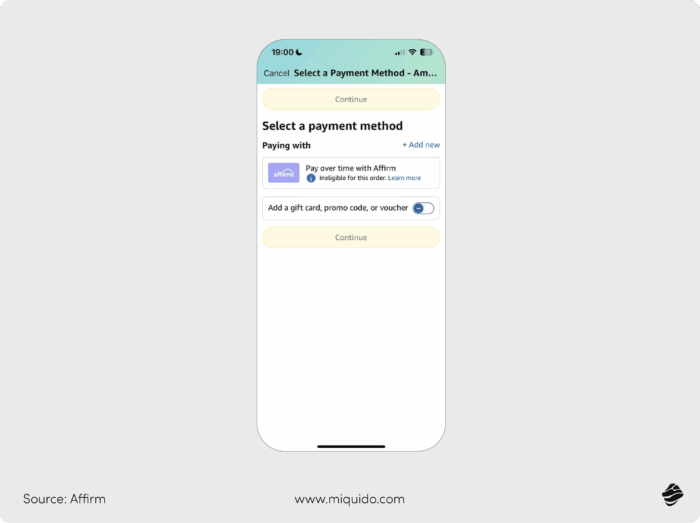
When customers check out, they see an option to “Buy Now, Pay Later.” If they choose this, the payment is divided into manageable chunks, often without requiring a credit check. The entire process happens instantly within the e-commerce platform, so there’s no need to apply for a separate loan.
In an example BNPL payment program below, the customer pays an initial installment upfront (25% of the total) at checkout, followed by three equal payments of 25% every two weeks, completing the full payment over six weeks.
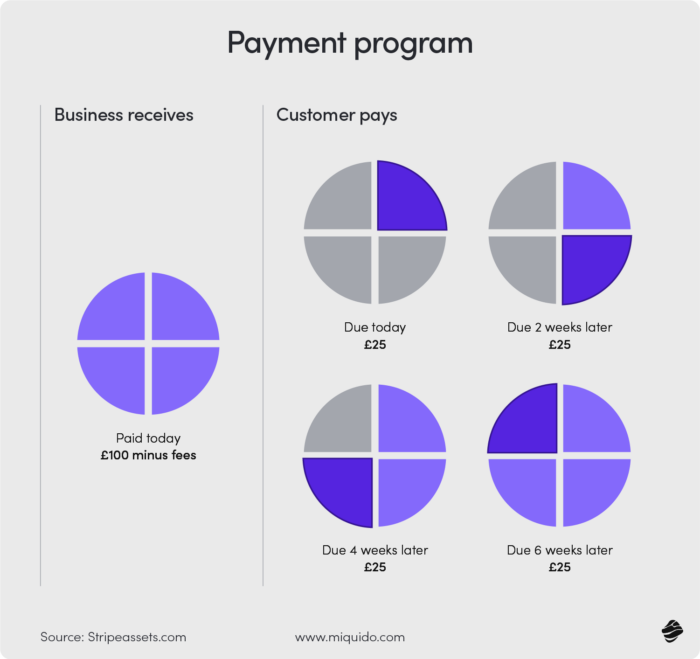
Some providers analyze past purchase behavior or alternative customer data to determine creditworthiness.
BNPL makes expensive purchases more manageable without requiring a credit card. Giving customers flexible payment options encourages more completed purchases, leading to higher conversion rates and increased average order values.
Point-of-Sale financing in retail
While BNPL is often used for smaller online purchases with shorter repayment terms, Point-of-Sale, or POS financing, is designed for high-value items like electronics, furniture, and appliances.
Many retailers, such as Apple, Home Depot, and Ikea, offer POS financing at checkout as one of their e-commerce app features or in stores.
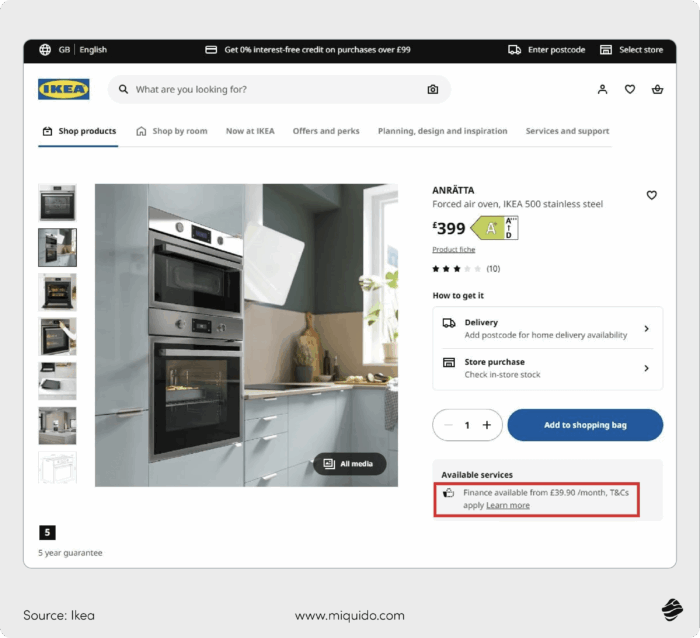
Instead of applying for a loan separately, customers are presented with financing options during the checkout process.
This process relies on real-time credit scoring and instant approvals. When a customer selects financing, the system communicates with lenders through an API. It retrieves financial data, evaluates credit risks, and provides a decision within seconds.
Payments are spread over several months, often with low or zero interest, which makes even expensive purchases more manageable.
For customers, this technology allows them to afford big-ticket items without waiting or saving up. For businesses, POS financing boosts sales, reduces cart abandonment, and attracts buyers who might hesitate due to the cost. Also, the ability to offer financing right at checkout helps keep customers within the retailer’s ecosystem.
Embedded banking
Embedded banking integrates financial services like digital wallets and in-app banking directly into platforms people already use. Instead of relying on traditional financial institutions, users can store, manage, and move money within apps that fit their needs.
The goal of embedded banking services is to provide tailored financial solutions for both business and private customers.
With banking-as-a-service, small business owners can separate personal and business finances by opening dedicated business payment accounts. If you’re a private customer, it becomes a convenient way to store, manage, and move money without needing multiple apps or accounts.
Embedded banking works through APIs that connect banking functionalities, like account creation, fund transfers, and transaction tracking, directly into non-financial platforms.
Here are two major examples of embedded finance in banking.
Digital wallets
Digital wallets like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and PayPal are extremely popular. 80% of Gen Z shoppers and two-thirds of Millennials use them.
These wallets have made payments faster and more secure. Instead of carrying cash or entering card details manually, users can store their payment methods digitally and pay with a tap.
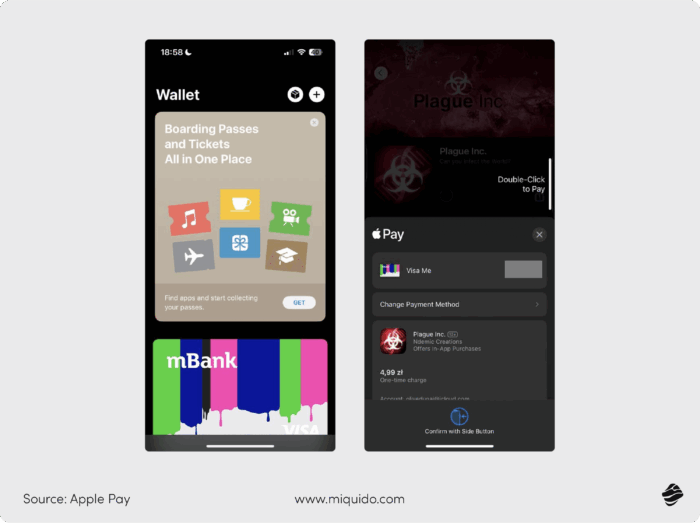
When making a purchase in a store, online, or within an app, customers simply select their digital wallet, and the payment is processed instantly.
Many digital wallets also support peer-to-peer transfers, which allow users to transfer money to friends and family with just a phone number or email. In physical stores, users can often switch between wallets at checkout, depending on their preferred payment method or available balance.
If you’re a consumer, digital wallets enhance security, eliminate the need for physical cards, and help you complete transactions much faster. Businesses offering digital wallet payment options also benefit through higher conversion rates, quicker checkouts, and reduced fraud risks.
In-app financial services
Some platforms go beyond simple payments and provide full banking-like services within their apps. These services include features like bill payments, tax calculations, and even savings tools. Users gain more financial control without relying on traditional banks.
For example, embedded bill payment functionality lets you settle utility bills directly within an app. Also, e-commerce businesses can integrate tax services that automatically calculate local taxes during the checkout process. This embedded finance example makes compliance seamless for both the business and the customer.
Other platforms, like Cash App and Revolut, offer users access to direct deposits, savings accounts, and even cryptocurrency trading. Such features simplify payments and money management, centralizing multiple financial activities in one place.
Offering in-app financial services makes our daily financial tasks much easier. It helps build strong customer relationships and boosts loyalty. Your customers will benefit from convenient money management and simplified bill and tax payments.
Embedded insurance
The insurance industry is undergoing a transformation, shifting from complex, time-consuming processes to seamless, on-demand coverage. In many cases, we don’t need to visit an insurance company or fill out lengthy applications. Embedded insurance programs let you purchase protection instantly within everyday digital platforms.
This is made possible through API-driven integrations that connect insurance providers with digital platforms. When a user makes a purchase, the system instantly retrieves relevant insurance options based on predefined rules. Machine learning models may also assess risk in real time, offering personalized coverage options without requiring lengthy approval processes.
Embedding insurance directly into transactions removes friction and gives customers the option to protect their purchases, trips, or services in real time.
Travel booking platforms
When booking a flight or hotel online, travelers often see an option to add travel insurance at checkout.
Travel booking platforms like Expedia, Booking.com, and Skyscanner embed insurance options directly into the booking process, offering an easy way to protect your trip.
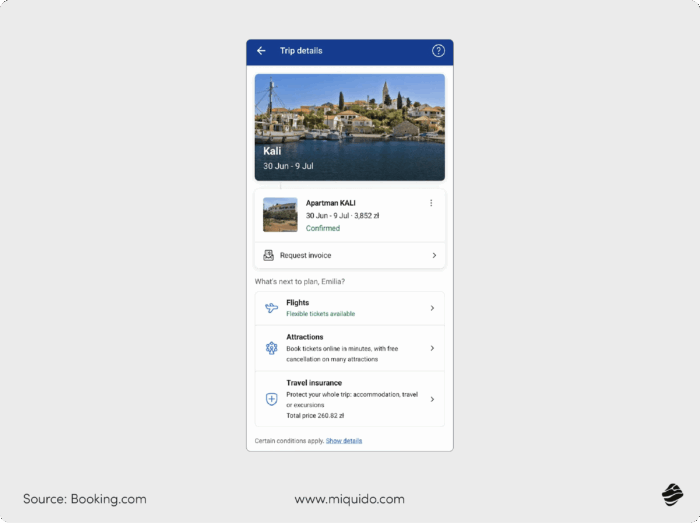
Instead of searching for a separate travel insurance provider, users can add coverage with one click. The insurance typically covers cancellations, medical emergencies, and lost baggage to provide peace of mind before a trip even begins.
Embedded insurance ensures travelers get the protection they need without the hassle of searching for insurance separately. For travel companies, this feature generates additional revenue. Since many customers wouldn’t seek coverage on their own, integrating it directly into the booking process leads to higher adoption rates.
E-commerce product protection
Many e-commerce platforms now offer extended warranties and protection plans when customers buy electronics, appliances, and other valuable items. One example is Walmart, which integrates a product care plan directly into its online checkout process.
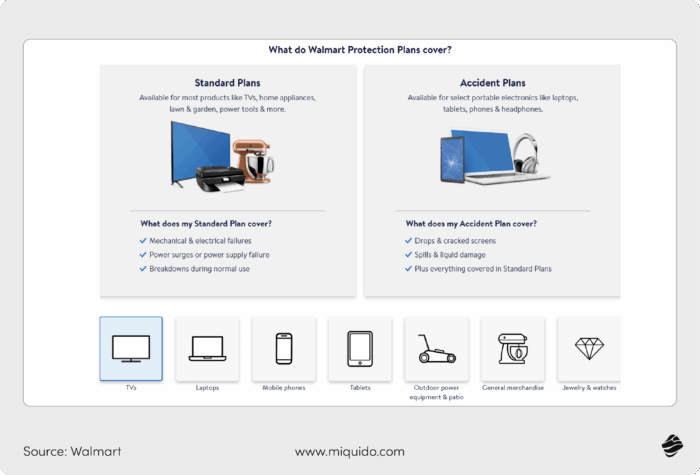
When a customer selects an eligible item, they are presented with an option to add a protection plan powered by third-party insurance providers. If they choose to include coverage, the policy is activated immediately upon purchase.
So, instead of dealing with a separate insurer, customers can file claims directly through Walmart’s platform.
With embedded insurance options, shoppers get a hassle-free way to protect expensive purchases while saving time on researching policies separately.
For retailers, it adds value to their products and generates additional revenue. Partnering with insurance providers allows e-commerce platforms to offer seamless protection plans without handling claims themselves.
Embedded investments
Investing is no longer limited to traditional brokerage accounts. Embedded investments allow users to access stocks, ETFs, and cryptocurrencies directly within the apps they already use daily. No more signing up for a separate platform. They can simply start an investing process with a few taps.
The embedded investments functionality simplifies the investment process, removing barriers that once kept many users from participating. Businesses benefit as well, as investment features generate transaction fees on investment activities, creating an additional revenue stream beyond their core services.
Here are two key embedded finance examples in investments.
Trading platforms
Apps like Robinhood, Cash App, and Revolut allow users to easily buy stocks and cryptocurrencies without going through a traditional brokerage. Trading platforms offer commission-free trades, instant deposits, and easy-to-use interfaces.

Rather than dealing with complex platforms, you can buy fractional shares, check stock performance, and even automate investments from your phone. Many platforms also integrate with social media, letting users follow trends and learn from experienced investors.
Embedded investing lowers the barrier to entry. Everyone can start building wealth without needing significant upfront capital. Additionally, if you’re a business, integrating trading features attracts a younger, tech-savvy audience and increases overall user engagement.
Robo-advisors
Robo-advisors are automated investment platforms that use algorithms to manage portfolios with little to no human intervention. An intelligent robo-advisor analyzes user data, assesses risk tolerance, and allocates funds across a diversified portfolio. Instead of requiring users to pick individual stocks, they provide a hands-off, goal-based approach to investing.
The process usually starts with a few questions about your financial goals upon registration. Based on the answers, the system creates and manages an investment portfolio, continuously adjusting asset allocations as needed.
This approach makes investing accessible to beginners who may lack the time or expertise to manage their own portfolios. Automation also reduces costs, making professional-grade investment strategies available at a fraction of the price of traditional financial advisors.
Consumers benefit from robo-advisors by gaining access to a structured, long-term investment strategy without the complexity of managing it themselves. Fintech companies, on the other hand, keep users engaged by offering seamless investment tools that encourage them to grow their wealth within the platform.
In closing
How do companies embed banking or finance programs into their own products or services?
The examples in this article show how large and small business owners can integrate value added financial services to improve customer experience, increase engagement, and unlock new revenue streams.
Digital platforms will play a pivotal role in financial services distribution. Therefore, your business must leverage embedded finance infrastructure to stay competitive.
For digital platforms, embedded financial solutions increase customer lifetime value (CLTV) and help retain customers as well as monetize the user base. Licensed financial institutions will enjoy better margins and gain access to a broader customer pool by partnering with platforms that already have strong user engagement.
The most exciting part is what this means for consumers. The embedded finance market makes financial services more accessible, affordable, and tailored to individual needs. Seamless payments, instant credit, and built-in investment tools will serve customers of all income levels.

![[header] 10 embedded finance examples](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/header-10-embedded-finance-examples.jpg)




![[header] how fintech is revolutionizing the music industry](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/header-how-fintech-is-revolutionizing-the-music-industry-432x288.jpg)

![[header] 10 embedded finance examples](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/header-10-embedded-finance-examples-432x288.jpg)