Last year, many headlines loudly proclaimed that 2023 would be the year of chatbots. And indeed, the development of genAI has prompted many companies to implement such a solution, especially in the banking sector.
Users are becoming accustomed to artificial intelligence, and banks are responding to this. According to eMarketer research, 48% of surveyed companies in the banking sector plan to use genAI to enhance interaction with chatbots in financial services. Many banks are now upgrading their solutions, taking advantage of this groundbreaking technology’s development and the increasing adoption of AI in fintech industry.
As Cornerstone Advisors report claims, only 22% of customers prefer a consultant over a bot because they prefer to speak to a live person. The most important reason cited by 40% of respondents is that they tried to find information online but could not. Therefore, implementing and improving chatbots is a good direction for banks, if only they focus on their effectiveness and usefulness.
How to do it? In our article, we break down the topic of chatbots in financial services into its components, examining best practices, successful case studies, and implementation challenges.
Why use chatbots for financial services
Banks were not always fond of chatbots, worrying about the customers’ reactions and technological obstacles. However, with the change in our habits and the genAI boom, today, their implementation is pure profit. What exactly do you gain?
Cost reduction
Implementing chatbots in financial services reduces the need for additional staff, reduces the number of errors, and eliminates costs associated with providing space and infrastructure for customer service. With chatbots, banks can scale their operations without additional investments.
Chatbots for financial services offer 24/7 customer service
Providing round-the-clock service by consultants is unprofitable for banks since they need to hire additional people to handle relatively few queries. It can also be challenging to compose and maintain a 24/7 team.
Chatbots in financial services allow banks to find a compromise – they increase customer satisfaction by providing customers with round-the-clock service without additional expenditure on staff.
Relief for the customer service department
Chatbots in financial services handle less complicated problems, allowing live consultants to focus on the most difficult ones instead of drowning in a flood of tasks.
As a result, service is faster, customer satisfaction rates increase, employees are under less time pressure, and their effectiveness increases. The number of errors, which cost the company money and reputation, also decreases.
Adaptation to the needs of new generations
Fewer and fewer users are accustomed to making phone calls or handling matters in person. To maintain a strong market position and prevent missed sales opportunities, banks must adapt to changing customer preferences, and chatbots in financial services enable this.
Quite a few advantages, isn’t it? However, remember that without effort, there are no rewards! To generate such benefits for a bank, you should take care of several technical aspects and apply a strategic approach to chatbot implementation.
What do you need to implement a successful chatbot?
Until recently, chatbot implementation involved creating conversation scenarios, which had many limitations, often discouraging users from interacting. While such chatbots could excel at solving standard problems, they struggled with unusual or more complicated ones.
What are chatbots today, or rather, what should they be to provide value? Large language models (LLMs) have allowed bots to go off the beaten path of the predefined scenarios. Thanks to NLU, they can immediately recognize the user’s intention and provide a relevant response regardless of the nature of the question. Meanwhile, banks do not have to rework scenarios with every change in policy or offer scope.
RAG infrastructure is crucial for efficient chatbot implementation
To enable such dynamic problem-solving by a chatbot, you can use the retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) framework, which connects the vectorized input of the user with relevant vectors in databases. This way, the bot will be able to incorporate current information from various sources into responses, providing a more accurate response and reducing the time spent on the entire interaction from the user’s side.

Efficient integration is crucial for effectively serving the customer in this model. The bank’s bot should be integrated via APIs with internal databases, servers, and the cloud. It should have access to information from various areas of the banking system, from the transfer register to transaction history and user account data and associated cards.
This way, it can effectively solve problems, such as blocked funds, unidentified expenses, or inability to pay by card. Additionally, it must be connected to the company’s knowledge base to efficiently respond to user questions, such as those related to company policy, lending, currency exchange, or savings accounts.
Implementing chatbots for financial services: good practices in 2024
Not all chatbots are created equal. Why do you gladly interact with some and avoid others like the plague? Although each chatbot should be tailored to the specifics and needs of the company, certain universal practices can increase its usefulness and improve the user experience.
Clear messages
Short text blocks, concise answers, bolding, clear graphic differentiation between chatbot and user messages – all of these elements positively affect the readability of interactions and facilitate the user in achieving their goal.
The language chatbot uses should be conversational and resemble a natural conversation rather than texts copied from a website or company policy. A well-trained bot can not only solve queries but also support company branding by using the company’s tone of voice.
Error prevention
Before executing an action, the chatbot should confirm whether all information is correct and whether the user actually wants to perform it. It is also worth implementing fallback mechanisms, which can save the situation when the chatbot cannot understand the user’s input.
Instead of hallucinating or providing responses, it should ask for clarification of the prompt, asking the user supporting questions. It should be goal-oriented – if it does not have absolute certainty about what the user wants, it should try to get to the heart of the matter instead of providing “substitute” answers.
Natural user path
Automatic suggestions were once considered good practice because, given the capabilities of chatbots at the time, they did indeed streamline the problem-solving process.
Today, users, accustomed to the flow of ChatGPT and other generative models, expect to receive a comprehensive answer without clicking and navigating through suggestions.
Redirections
Even the best chatbot is not always able to replace a live consultant, and the user should have the option to choose who to talk to. A good practice is to automatically redirect to a consultant if the user writes that they want to talk to them. It is also good to differentiate between chatting with a chatbot and a consultant by including their name, function, and photo in the chat interface.

Well-thought-out visual identification of the chatbot for financial services
Looking at most bots, not only in the banking sector, you will notice that they are not associated with humans in any way. This is a security measure for companies – the user should be aware that they are talking to a bot.
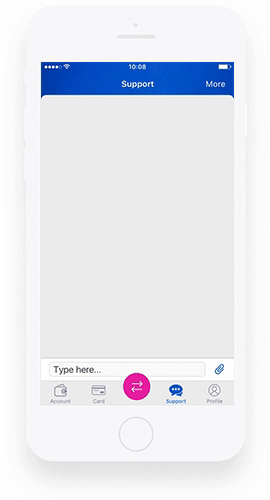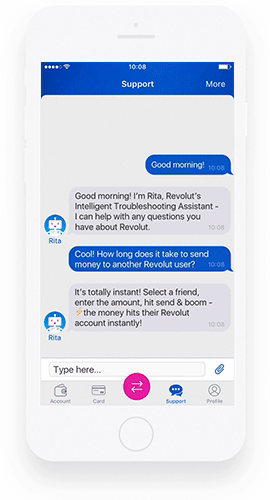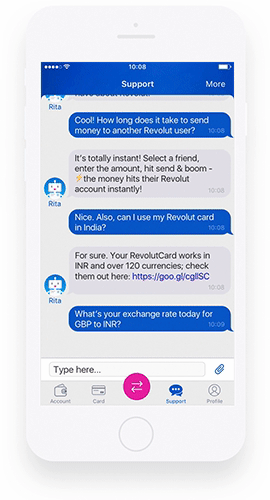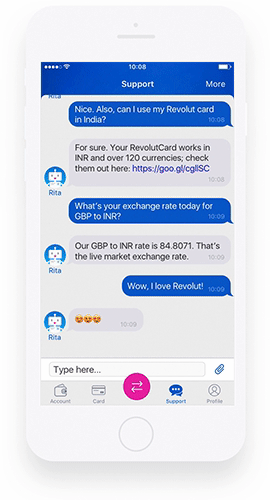
That’s because they may approach it in a suitable way and moderate the response to make it better understood. A well-designed chatbot can also become an integral part of brand identification. Eno from Capital One or Rita from Revolut are examples of bots that combine these two imperatives well.
Allowing feedback
Feedback is crucial for improving your bot and services in general – it is worth using every interaction to obtain it. You can ask if the interaction was helpful or go a step further and allow comments.
How will chatbots in financial services evolve?
A big part of larger banks worldwide use chatbots or virtual assistants (including voice assistants) to some extent. Among the customer-favored chatbots in financial services, we can mention Rita from Revolut or Amy from HSBC.
However, in many cases, these are older solutions based on established scenarios that redirect most cases to live consultants. It is a “safe” choice but not necessarily forward-looking and profitable.
Use cases of chatbots in financial services
An interesting exception here is ING, which rebuilt its virtual assistant in collaboration with McKinsey, using GenAI technology. The improved flow (instant response based on intention) allows problems to be solved faster and on a larger scale.
Tests of the tool on ING clients in the Netherlands showed that the new chatbot effectively served 20% more clients than its classic, older cousin. Bunq also relied on GenAI by implementing Pascal, the first European chatbot based on this technology.
The future of chatbots for financial services
In the near future, we will undoubtedly witness many similar transformations as users become accustomed to a new, more natural, and efficient form of interaction. Many banks will probably choose the same path as mentioned ING or Bunq, facing increasing competition in banking customer service, and use genAI as a shield.
Banking chatbots will become more of assistants, helping customers proceed with various tasks and understand their spending patterns, as well as future financial perspectives. As GenAI’s capabilities expand, we will see the answers become more versatile, with automatically generated video instructions, and personalized recommendations based on user data.

Is chatbot for financial services the future?
Aside from faster and improved service, chatbots bring one other crucial benefit – cultivating inclusivity. With digitalization, the number of physical headquarters has been gradually decreasing – as this process continues, chatbots will enable the banks to stay inclusive, providing customers with a substitute for a consulting visit.
In the underserved or unbanked areas, they give customers equal access to information, problem-solving, and financial advice. Those who are not very familiar with technology do not have to wander around the app or website – the chatbot helps them to solve their problem quickly without delving into technological intricacies.
Customer service jobs are an important pillar of the job market, particularly in the outsourcing hubs like the Philippines, India, Malaysia, and Brazil. With the shift towards the implementation of AI in business, the working landscape in this area will have to change.
It does not mean that chatbots will replace the human workforce, but rather that the scope of their service will radically change, with a stronger focus on specialization.
Challenges in implementing chatbot for financial services and how to tackle them
To maximize the benefits of implementing a chatbot in a company, you should start by addressing key challenges that banks face.
Data security in chatbots for financial services
Since the chatbot uses corporate data, advanced security measures are essential to customer safety. Banks should encrypt both stored data and the one exchanged between the bot and the user. It’s also worth considering additional authentication to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
The interactions between the chatbot and users should be continuously monitored by AI for any unusual activity, cyberattacks, or data breaches. Prevention is always better than cure, so it’s worthwhile subjecting the chatbot to regular stress tests to check its resilience to data leaks and other abuses.
Cyberattacks have been intensifying in recent years, but the development of predictive analytics in fintech has also progressed a lot – so worry not, chatbots can be as safe as any other solution if you take appropriate measures!
Privacy policies
Many customers fear sharing sensitive information with the chatbot due to its possible use in model training. The bank should inform them precisely how their data is used and stored to dispel doubts that could prevent them from interacting with the bots, especially with the current genAI development.
Also, as with any other solution processing data, chatbots are subject to privacy policies (like GDPR). Every bank should make sure its construction reflects the current norms to avoid costly fines and loss of trust.
As an AI chatbot development company, we can help you solve these and other challenges related to data processing and infrastructure, building a chatbot that customers want to use and interact with.
Providing extensive Artificial Intelligence app development and Generative AI services for the financial sector, we can boost your customer service with a tailor-made solution that both generates savings and secures clients’ trust. Reach out to us to talk about your needs!








