While global industry business leaders are rushing to adopt AI, the manufacturing industry is taking time to fully embrace innovation. The main barriers? Investment, scale, training. But the change is gaining momentum – as of 2025, over 77% of manufacturers have implemented AI solutions, marking an increase from 70% in 2023.
The geopolitical landscape impacting supply chains, the swinging economy, shifts in main manufacturing global powers, and new sustainability norms – in such conditions, AI is turning into a necessity. The perks are undeniable. So, what exactly makes AI such a game-changer in manufacturing? Let’s take a closer look at how different companies maximize their benefits from AI implementation.
Overview of AI integration in manufacturing
In 2024, 41% of manufacturers expected AI to drive growth, a figure projected to rise to 61% by 2029. Before the GenAI boom and the accessibility of open LLM models, the adoption of AI in manufacturing mainly focused on the automation of assembly lines and data integration.
Now, the possibilities are even wider: at an incomparably low cost, manufacturers can integrate AI solutions for generative design, document management, decision-making support, and much more.
Significance of AI in modern production
The shift towards AI in manufacturing seems inevitable in today’s economic landscape, where the workforce is shrinking, trade tensions and tariffs make expenses more unpredictable, energy prices are rising, and climate change may soon impact transport routes and access to various resources. How can companies stay ahead of these challenges? The answer lies in AI.
Manufacturing leaders are not hesitating to implement it in various areas, from AI for production planning to waste management. As an essential element of Industry 4.0, AI, together with the Industrial IoT and cloud computing, enables factories to combine all the data from sensors, ERP systems, supply chains, and machinery to extract key insights in real time. It often uncovers previously hidden inefficiencies and bottlenecks, paving the way towards faster, cost-effective production cycles.
Enhancing operational efficiency
AI enhances efficiency by detecting issues before they escalate, eliminating human errors, and making precise predictions that support planning and maintenance. It prevents situations where a missing component or an unexpected machine failure causes costly downtime.
The result? Substantial savings. Take a look at Bosch, which has been leading automation in its sector for years. “Our new AI solution will save plants millions in costs,” claims Dr. Michael Bolle, Bosch CDO/CTO, in an official press release. Predictions confirm that: after investing 500 million euros in automation and digitization in its plants, Bosch will save twice as much – roughly one billion euros – already by 2025.
No wonder the company keeps its steady course towards AI implementation and its expansion in key operational areas. By 2025, the aim is for all Bosch products to either contain AI or have been developed or manufactured with its help.
Process automation
Streamlining repetitive tasks is one of AI’s strongest suits. Let’s take an example of process automation in the joinery industry. AI can control CNC machines full-time – a key aspect of product quality and machine longevity that is very error-prone and repetitive:
- AI systems integrated with the CNCs optimize router tool paths to minimize cutting time and tool wear .
- AI systems integrated with sensors monitor CNC machine vibration, temperature, and load to predict failures and schedule maintenance before breakdowns, and adjusts cutting speeds based on real-time wood grain and hardness detection.
- AI-powered cameras detect wood defects (knots, cracks, grain inconsistencies) before processing and measure cut pieces to ensure accuracy within tolerance limits.
Full automation of the manufacturing process is far from becoming a standard, but some companies are taking bold steps, with China leading the way. The market conditions call for this, with Reuters reporting that China’s working-age population could shrink by around 6% by 2030.
Aligning with this trend, Xiaomi unveiled its “dark factory” in Changping, a fully automated, AI-driven manufacturing facility that operates without human intervention. The factory produces one smartphone per second, eliminating human errors and optimizing performance through real-time communication and self-developed AI systems.
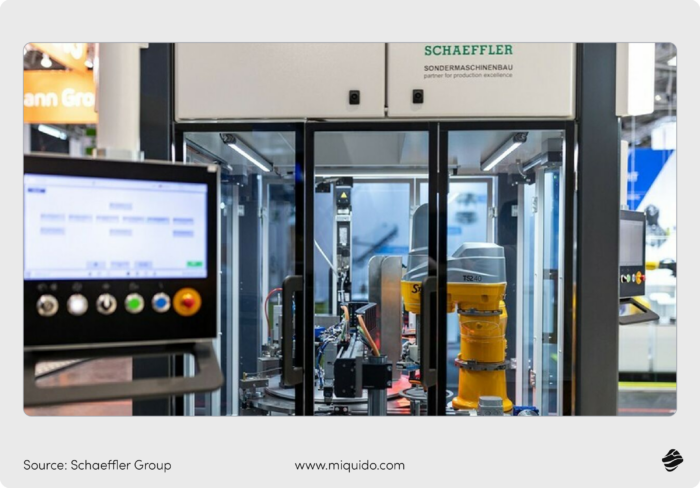
Reducing human error is crucial, especially in manufacturing processes of very sensitive products, where even a one-millimeter miscalculation can make the end result unsellable. AI can, for instance, support engineers in generating code for PLCs faster and error-free, like Siemens’ Industrial Copilot adopted by Schaeffler.
The Industrial Copilot helps Schaeffler’s automation engineers generate code for programmable logic controllers (PLC), which control most machines in factories worldwide. Engineering teams can significantly reduce time, effort, and the probability of errors by generating PLC code through natural language inputs.

Predictive maintenance
AI-powered predictive maintenance solutions allow manufacturers to anticipate equipment failures and avoid costly disruptions. The savings from such AI application can be significant, as the example of BMW shows. In January 2024, BMW implemented an AI-supported predictive maintenance system to monitor conveyor technology during vehicle assembly. This integrated, learning maintenance system identifies potential faults early, preventing over 500 minutes of assembly disruption annually.
Minimizing downtime is critical for modern factories, where every minute of inactivity leads to financial losses. AI can help Schaeffler became one of the first users of Microsoft’s Factory Operations Agent, a new product powered by large language models and designed specifically for manufacturers. The chatbot-style tool helps track down the causes of defects, downtime, or excess energy consumption, acting like ChatGPT for factories with OpenAI’s models operating in the backend through Microsoft Azure.
Improving product quality
Without continuous product quality improvement, gaining competitive advantage in manufacturing is impossible. A AI revolutionizes quality control by ensuring consistent standards and detecting defects in real time. AI-powered cameras inspect products for imperfections, reducing waste and ensuring only flawless items reach customers.
Automated systems continuously refine manufacturing processes, reducing errors and enhancing product consistency. As a result, companies achieve better customer satisfaction, fewer returns, and higher operational efficiency.
Generative design can put a manufacturer a few steps ahead of competition, facilitating personalization and efficient resources usage. Imagine your favorite shoe company could actually make the design exactly how you want it – not just customizing colors and textures, but modifying shapes and various other aspects. Generative design makes it happen at no cost and with minimal resource use.
AI optimizes product designs by finding ways to use materials efficiently, reducing costs while maintaining quality. The manufacturer can, for instance, integrate generative AI with different social media and eCommerce channels to detect product defects in reviews and automatically suggest alternative designs that align with company goals.
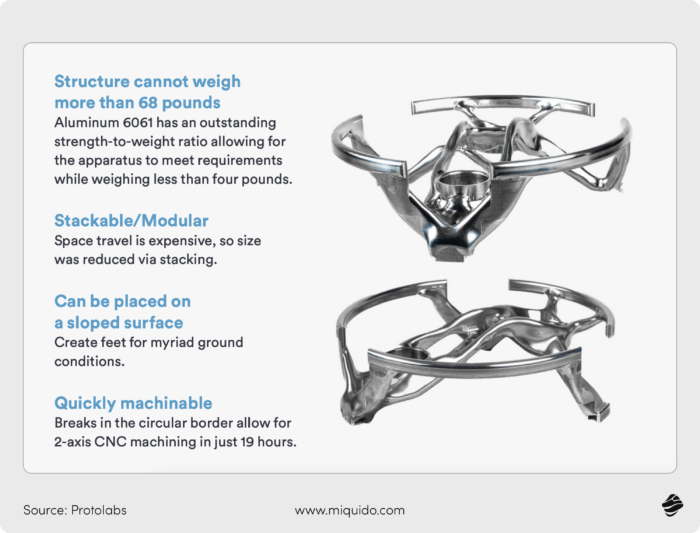
Contrary to common belief, generative AI can be a perfect partner for special assignments, even so complex as spacecraft. In July 2024, Protolabs collaborated with NASA engineers to rapidly manufacture a generatively designed space travel apparatus for collecting gas samples released by sunlight hitting the moon. Utilizing digital manufacturing techniques, Protolabs delivered the part within 36 hours, demonstrating the efficiency and speed of generative design in aerospace applications.
Optimizing supply chain management
In today’s economic and geopolitical landscape, with tariffs, climate change, and globally spread conflicts affecting supply chains, AI in manufacturing is more essential than ever. Just in the last few years, several major events have blocked or slowed down key transport routes, cutting off manufacturers’ access to resources.
Without accurate machine learning predictions, manufacturers risk excess inventory—leading to unnecessary costs and logistics challenges—or, conversely, product shortages that could harm their reputation and business relationships.
Demand forecasting and AI in production planning is one way companies can achieve supply chain optimization, adjusting production levels and order volumes to match current and future conditions. AI systems process data from across the supply chain, continuously refining demand forecasts. These insights integrate seamlessly with production process planning software, automatically adjusting planned orders and the number of products leaving the assembly line each day.
Additionally, AI supports logistics optimization by analyzing traffic, weather, and delivery schedules to select the best shipping routes. The system then assigns these optimized routes to drivers, cutting transportation costs and minimizing delays.
Enhancing workplace safety
Just a hundred years ago, struggling with respiratory diseases, industrial accidents, and the effects of toxic substance exposure was an everyday reality for the average worker. Fifty years later, conditions improved, but physical strain remained a major issue—workers were still exposed to carcinogenic substances and suffered long-term health effects from working in unhealthy positions.
Today, our awareness of manufacturing-related health risks is significantly higher, reflected in stricter safety regulations. However, assembly line workers still face various threats. AI enables effective hazard identification, continuously monitoring key elements of the assembly line and factory for potential risks, such as:
- Machinery performance and malfunctions
- Worker posture and repetitive strain levels
- Air quality and toxic gas leaks
- Temperature fluctuations and fire hazards
- Electrical systems and overload risks
- Product defects and quality control issues
AI-powered systems gather data from these points, issuing alerts whenever potential danger arises, allowing for real-time intervention to prevent accidents.
Beyond hazard identification, manufacturers are increasingly integrating cobots—collaborative AI powered robots that replace humans in the most demanding and repetitive tasks, providing cost and safety benefits. Cobots help reduce physical strain and assist in hazardous manufacturing tasks, such as:
- Handling heavy or dangerous materials (e.g., molten metals, sharp objects)
- Operating in high-risk environments (e.g., extreme temperatures, confined spaces)
- Exposure to harmful chemicals (e.g., toxic fumes, corrosive substances)
It’s no surprise that cobots are becoming essential on assembly lines worldwide. A prime example is the global healthcare manufacturer Sanofi, which has integrated cobots at the end of its production line to assist with product packaging. By lifting product packages weighing 3-8 kg, the cobot has significantly reduced ergonomic risks for workers—each unit lifts between 300-700 kg per day, improving both efficiency and workplace safety.
embed video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DZGpGX17Hwg
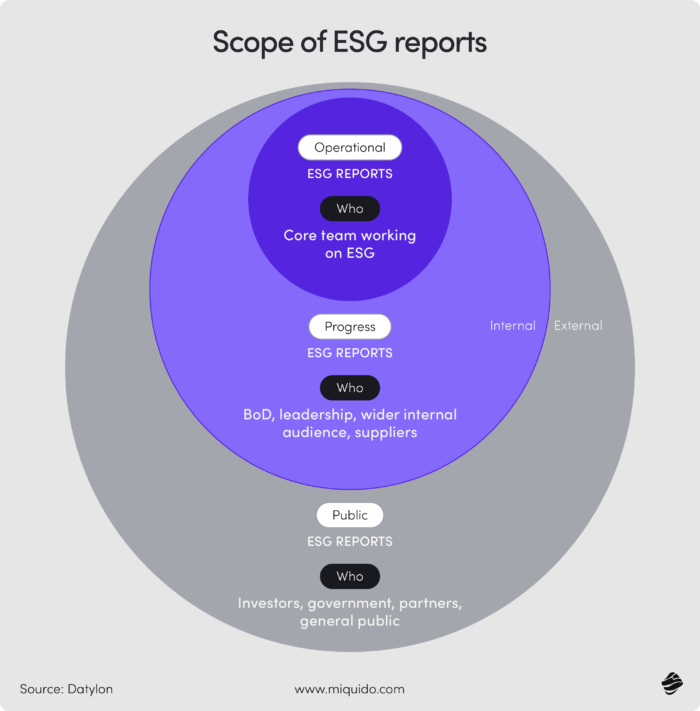
Facilitating sustainable manufacturing
In the era of climate crisis, increasingly strict CO₂ emission standards are becoming the norm — not just in the European Union, but across the entire globe. While the United States has recently started rolling back some environmental regulations and shifting focus toward non-renewable energy sources, China in 2024 implemented new regulations concerning the carbon emissions market.
To comply with these evolving standards, gradually reduce emissions, and accurately report environmental impact across the entire supply chain, AI is becoming indispensable. Artificial intelligence can track emissions at every stage — from raw material sourcing and production to logistics and final delivery. It enables real-time monitoring, automates report generation, and helps identify the most emission-heavy processes, empowering companies to make data-driven decisions toward sustainability goals.
Energy management
A typical large factory consumes 1 to 5 megawatts (MW) of energy per day, powering a wide range of essential manufacturing operations. These include heating and cooling systems, lighting, machine operations on the assembly line, material handling, air compression, and IT infrastructure. With so many variables involved, finding solutions that optimize energy consumption while aligning with a company’s operational and financial goals can be a challenge.
This is where artificial intelligence steps in. AI can collect and analyze real-time data regarding energy usage throughout the entire facility, identifying inefficiencies and recommending adjustments that ensure maximum efficiency while reducing operational costs. It can detect energy leaks, overconsumption caused by outdated or poorly maintained machinery, or even suboptimal process scheduling—for example, running all high-power equipment simultaneously during peak hours.
In addition to cost savings, manufacturers are using AI models to reduce their environmental impact. By performing complex calculations, AI can estimate the carbon footprint of specific manufacturing processes and offer the simplest, most effective strategies to reduce emissions in high-impact areas.
For instance, a large automotive plant may discover that its paint shop ventilation system consumes excessive energy and emits high levels of CO₂ due to inefficient airflow management. With AI-driven insights, the plant could automate ventilation control based on real-time air quality data, significantly cutting both energy use and emissions. In another case, AI-driven predictive maintenance may detect performance drops in a key component sourced from a third-party supplier, prompting an early replacement and avoiding excess emissions across the supply chain.
Waste reduction
Aside from reducing emissions, AI-driven systems can also help manufacturing companies minimize waste. Until recently, the role of AI in waste management focused mainly on identifying operational areas that generate the most waste and suggesting improvements based on these insights.
A factory could discover, for instance, that a faulty component is causing a microdefect that disrupts the assembly process, leading to finished products failing quality assessment. AI can resolve the problem by using computer vision to detect defects earlier in the production process and applying predictive maintenance to fix or replace the faulty component before it causes further disruptions.
But there is much more to its AI capabilities. Generative design, a technique powered by smart manufacturing systems, can take waste reduction to a whole new level. For example, when designing a metal component, GenAI can generate hundreds of design variations optimized for material efficiency. The system then selects the version that uses the least amount of raw material while maintaining strength and durability, significantly reducing scrap without compromising quality.
Access the key benefits of AI in manufacturing with tailored software
As you can see, the positive impact of manufacturing AI is broad, streamlining both factory floor and back office processes. A manufacturing business can incorporate AI tools in various operational areas, from the assembly line and quality control process to inventory management.
On top of that, by analyzing historical sales data to understand market trends and adjust their production volumes to them, avoiding excess inventory or deficits. Recent trends in manufacturing definetely show that AI is here to stay.
Manufacturing sector is implementing AI at an increasing pace, both through complex systemic upgrades and simpler automations with GenAI, which you can implement at the fraction of costs with our AI Kickstarter. Let’s discuss your needs and find the most cost-effective solution.

![[header] exploring the key benefits of ai in manufacturing industry](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/header-exploring-the-key-benefits-of-ai-in-manufacturing-industry.jpg)


![[header] case study b2b system development and product configurator implementation
in industry 4.0](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/header-case-study_-b2b-system-development-and-product-configurator-implementation
in-industry-4.0-432x288.jpg)

![[header] exploring the key benefits of ai in manufacturing industry](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/header-exploring-the-key-benefits-of-ai-in-manufacturing-industry-432x288.jpg)
![[header] woodworking automation – how joinery industry is growing with digital transformation which is right for your project](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/header-woodworking-automation-–-how-joinery-industry-is-growing-with-digital-transformation-which-is-right-for-your-project-432x288.jpg)