Often, when discussing AI in manufacturing operations, we focus on massive modernization efforts. While these are increasingly common and deliver tremendous benefits, AI applications in manufacturing go far beyond robotics and predictive analytics.
Many implementations are relatively straightforward, don’t require major facility changes or new equipment, yet deliver radical benefits. Take Eaton and its 87% reduction in design time for automated lighting or General Motors achieving 40% lighter and 20% stronger components using AI systems.
AI in manufacturing isn’t limited to multi-million dollar projects. AI-driven predictive maintenance, sales support system modernization, generative technologies facilitating innovation – these AI solutions are available for any production company. In our article showcasing use cases, we present both the low-hanging fruit and innovations requiring more structural changes to infrastructure and software.
The manufacturing industry values concrete results, so we describe each use case based on real-life implementations in successful companies. Discover how they achieved impressive results and fully leveraged artificial intelligence technologies while reducing maintenance costs.
B2B eCommerce platforms and configurators powered by artificial intelligence
Many manufacturing companies face a similar challenge: sales still occur through traditional channels using manual methods. This can lead to customer-side errors and problems – for example, purchased products cannot be delivered on time due to inventory shortages, or payment processing issues arise due to missing data.
These issues are particularly visible when manufacturers rely on just-in-time production models. That means orders are only manufactured once payment is received, adding pressure to payment processing speed. On top of that, many manufacturers export globally, requiring multilingual support for sales, customer service, and documentation.
A well-designed B2B platform with integrated AI and Generative AI features can solve these problems:
- real-time automated inventory updates protect customers from delayed deliveries
- automated order and payment processing prevents delays and misunderstandings on both sides
- built-in manufacturing smart product configurator allows clients to examine the final product from every angle before production, preventing complaints and reducing material waste
- multilingual chatbots and automated translation allows to adjust to global customers’ needs at no effort
As our analysis of automation in joinery market shows, more companies are implementing these improvements. It’s a relatively simple implementation of AI in manufacturing, and we will likely see its increased adoption in the following years.
Generative design with AI tools
Now it’s time for a use case particularly popular among automotive and medical device manufacturers. As Generative AI develops and becomes more accessible, it can support innovation and design efficiency at ever-lower costs. Simultaneously, it helps continuously improve products, even the most specialized ones. For example, manufacturing companies can easily consolidate parts to reduce potential points of failure, utilize tailored geometries based on medical scans, and achieve incredible resistance.
NASA engineers demonstrated this power during the Power Source Global Summit, where they developed an Evolved Structure for the Artemis lunar program. Participants used generative design to create apparatus that could withstand extreme temperature fluctuations from -315°F to -55°F (-193°C to -48°C) while effectively holding sample collection containers.
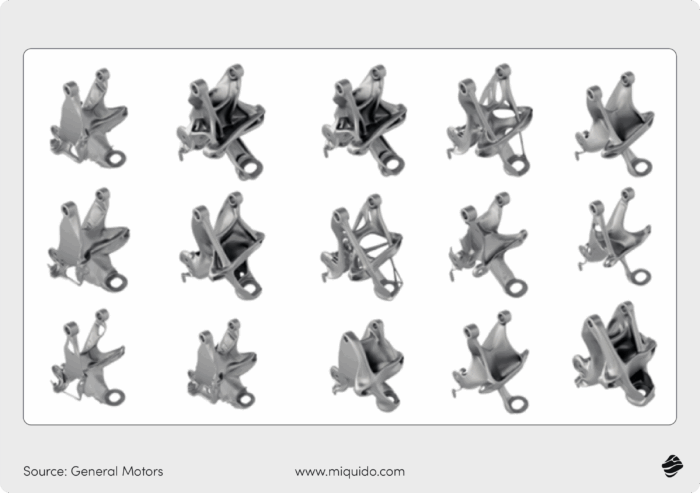
In the automotive sector, GM’s collaboration with Autodesk yielded remarkable results. By applying generative design software to vehicle components, they created a seat bracket that’s 40% lighter and 20% stronger than the original. This innovation consolidated eight separate parts into a single 3D-printed piece, dramatically improving material efficiency and structural integrity.
Similarly, Eaton has revolutionized its product development through generative AI. Their achievements are striking: design time for an automated lighting fixture reduced by 87%, weight of a liquid-to-air heat exchanger minimized by 80%, and design time for a high-speed gear lowered by 65%. These improvements showcase how AI can dramatically accelerate development while optimizing performance metrics.
For footwear innovation, Salomon’s SolScan technology quickly captures and combines shoe images to create detailed 3D models, with AI supporting image generation and data processing. The resulting point cloud enables precise measurement of any dimensions on the scanned object, streamlining the design and quality control process.
Whether optimizing spacecraft components, automotive parts, industrial equipment, or consumer products, generative design consistently delivers faster development cycles, material optimization, and performance improvements—making it an essential AI application for manufacturers seeking to maintain competitive advantage in today’s rapidly evolving marketplace.
Digital twins
Operating in a massive manufacturing facility makes it challenging to see everything at once. That is, until you fully harness the power of AI, with digital twin being the ultimate goal. Digital twins represent the holy grail in manufacturing and logistics industries, where all manufacturing processes form an interconnected network.
By collecting data from all systems and sensors, digital twins mirror the real-time state of manufacturing units, allowing production managers and line supervisors to address issues before they escalate. They highlight inefficiencies and potential improvements that are easily overlooked at the macro scale and supports predictive maintenance as well as effective quality control.
Electrolux’s partnership with Siemens Digital Industries demonstrates digital twins’ transformative potential. By implementing Siemens’ Plant Simulation software, they created virtual replicas of their production facilities, enabling detailed analysis and enhancement of critical processes like refrigerator wall foaming. This approach delivered remarkable results—approximately $2 million in savings through optimized conveyor and warehouse configurations alone.

Taking digital twins to the next level, Siemens has pioneered their integration across diverse industrial applications. Their collaboration with tech powerhouses like Nvidia and AWS showcases the technology’s versatility and growing sophistication. One standout example is their work with Freyr, a clean battery solutions provider, where they modeled and optimized battery plant operations before breaking ground on construction.
Companies can also use digital twins for the purpose of complex operational failure detection, as the example of JFE shows. Using biomass power generation, they need to monitor the related processes constantly, as any failure could paralyze the operations across the unit. By extracting huge amount of operational data, their digital twin visualizes the insights and identify patterns, indicating any abnormalities, so that the human workers can react and make decisions in an instant.
Unlike traditional planning methods that rely on educated guesses, digital twins offer data-driven decision-making opportunities that dramatically reduce risk and increase operational excellence. Companies across manufacturing sectors—from consumer appliances to advanced energy storage—are realizing significant ROI through improved resource allocation, reduced downtime, more accurate demand forecasting, optimized processes, and accelerated innovation cycles.
Autonomous inventory audits and quality control
Quality control and inventory management are tedious, repetitive tasks. Even the most trained human eye can miss critical details, especially after hours of work. Extended periods of visual tasks cause oculomotor fatigue, affecting focus and visual processing accuracy. Combined with mental fatigue affecting attention and decision-making, we have a ticking time bomb.
Automation tackles these issues head-on, with drones equipped with advanced imaging and data processing capabilities leading the way. They deliver consistent performance without fatigue and can operate in challenging or unsafe environments. This also eliminates logistical problems—manufacturers can optimize warehouse space without concerns about worker safety and comfort.
Although the use cases we gathered focus on logistics companies, that are pioneering drone automation, they easily could find their application in manufacturing units and their warehouses.
Wagner Logistics demonstrates the financial impact of this technology. Their Monroe, Louisiana facility deployed Gather AI’s autonomous drones that systematically fly through the warehouse, capturing images and comparing inventory with their management system in real-time. The results were immediate and significant—cutting inventory count time in half while reducing errors by 50%, translating to approximately one million dollars in saved product value.

While Wagner focused on efficiency and error reduction, Romark Logistics pushed the technology even further toward precision. Using similar drone technology but emphasizing data verification, they achieved an exceptional fivefold improvement in inventory processes with near-perfect 99.9% accuracy. Their drones not only capture product images but also read barcodes and perform instant verification, creating a comprehensive inventory management solution that dramatically enhances operational reliability.
Taking a different approach focused primarily on worker safety, Barrett Distribution targeted high-risk manual tasks with their drone implementation. By eliminating dangerous inventory checks at elevated heights, they not only protected their workforce but also unlocked operational benefits—freeing six dedicated cycle counters for more valuable tasks while saving $250,000 in material handling equipment costs. Their solution demonstrates how safety improvements and business efficiency can go hand-in-hand.

Fully automated assembly lines
A factory where machines operate independently without any supervision, and where you won’t find a single person around the assembly line is no longer a vision of the future. Just look at Xiaomi and its pioneering smart factory with high precision assembly line, operational since 2023. The company saves enormous sums on workforce costs while operating in a much more sustainable way – lights-out manufacturing radically reduces electricity consumption.
Although fully automated factories remain the exception, many companies use automation and AI-powered robots to implement autonomous production lines. This solution simultaneously leverages multiple benefits of AI in manufacturing – increased efficiency and production speed, reduced errors and employee expenses, as well as lower injury risks.
In October 2024, Airtificial showcased the industrial scale of this revolution with its largest assembly line yet—a 100-meter-long robotic and intelligent system for assembling cooling systems for electric and hybrid vehicle batteries. This €5.2 million project for a leading German Tier 1 automotive supplier features 20 robotic arms coordinating with over 15 vision cameras, all powered by deep learning algorithms that perform real-time analysis and quality control.
While Airtificial built their system from the ground up, Ford took a different approach by enhancing existing infrastructure. At their Livonia, Michigan transmission plant, Ford integrated Symbio Robotics’ AI technology to optimize operations. The system continuously learns from previous assembly attempts, fine-tuning robotic arm movements to increase torque converter assembly speed by 15%. This implementation demonstrates how AI can incrementally boost automated processes without requiring complete factory redesigns.
Moving from large vehicle components to intricate parts handling, a major European automotive air conditioning systems manufacturer deployed Solomon’s AI-powered AccuPick 3D bin picking software paired with SolScan 3D cameras. This sophisticated solution tackles one of automation’s greatest challenges—recognizing and handling complex, overlapping components with precision tolerances under 1 mm. The system reduced cycle times to under 5 seconds per component while optimizing space utilization within the assembly line.

Carbon footprint reduction
The pressure to reduce carbon footprint in the manufacturing industry grows increasingly intense. It’s no longer just about reputation and building future-oriented partnerships, but also about stringent reporting requirements and purchasing emission rights.
Meanwhile, final emissions comprise numerous factors—from the energy efficiency of factory equipment, through waste and defective products created on manufacturing processes, to the selection of materials, suppliers, and partners at various stages of the supply chain management.
Implementing AI is irreplaceable in identifying opportunities to reduce emissions and inefficiencies that inflate a company’s carbon footprint. It also helps with sustainability-oriented supply chain optimization and hassle-free fulfillment of ESG reporting obligations and compliance control.
Walmart demonstrates AI’s power in addressing sustainability challenges at massive scale. Their Eden system employs machine learning and computer vision to monitor food products’ shelf life, aiming to eliminate an astounding $2 billion in food waste. Beyond inventory management, Walmart also leverages AI to optimize delivery routes, significantly reducing fuel consumption and associated emissions. This dual approach tackles both product waste and transportation inefficiency—two major contributors to retail’s environmental impact.
Chatbots and knowledge bases
Another example of generative AI in manufacturing is chatbots and knowledge bases supporting employees in creative and text-based tasks. While they’re primarily associated with customer service, they can also serve internal purposes, enabling effective onboarding, training, and problem-solving in an intuitive, conversational way. Instead of digging through millions of materials, many requiring specific permissions, employees can quickly resolve their doubts.
Wienerberger Austria demonstrates this approach’s practical value in addressing a common manufacturing challenge: the excessive manual work required to handle customer inquiries about product compatibility. Previously, office staff had to tediously compare multiple product data sheets by hand—a time-consuming process prone to human error.
Their solution leverages a Large Language Model (LLM) “fed” with internal company data, enabling targeted processing of customer inquiries through an AI-supported chat system. This not only accelerates response times but also ensures consistent, accurate information delivery.
AI solutions for production planning and scheduling
Manufacturing AI transforms production planning by instantly evaluating countless schedule combinations, far outpacing human workers when handling last-minute order changes and equipment malfunctions. When disruptions strike—like a blocked supply route threatening production—these AI solutions immediately recalibrate everything to keep operations flowing smoothly.
Machine learning and AI for production planning identify critical patterns by analyzing which production lines excel with specific products or which suppliers consistently cause problems. This transforms manufacturing from guesswork to confident execution, optimizing workflows while predicting future demands and maximizing equipment capacity.
Lenovo proves the financial impact with their AI-powered scheduling system that revolutionized their supply chain. The numbers tell the story: 24% increased production capacity, 19% higher production volumes, and on-time deliveries improved 3.5 times—directly boosting both profits and customer satisfaction through intelligent predictive maintenance.
Manufacturing AI tailored for your needs
Every manufacturing business today needs digitalization, but the key is adjusting AI technologies to the specifics of your business. With Miquido as an experienced Industry 4.0 software development partner, you can introduce innovations that will make real difference.

![[header] top ai use cases in manufacturing](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/header-top-ai-use-cases-in-manufacturing.jpg)


![[header] top ai use cases in manufacturing](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/header-top-ai-use-cases-in-manufacturing-432x288.jpg)


![[header] case study b2b system development and product configurator implementation
in industry 4.0](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/header-case-study_-b2b-system-development-and-product-configurator-implementation
in-industry-4.0-432x288.jpg)
