

Generative AI Guardrails Definition
Generative AI Guardrails
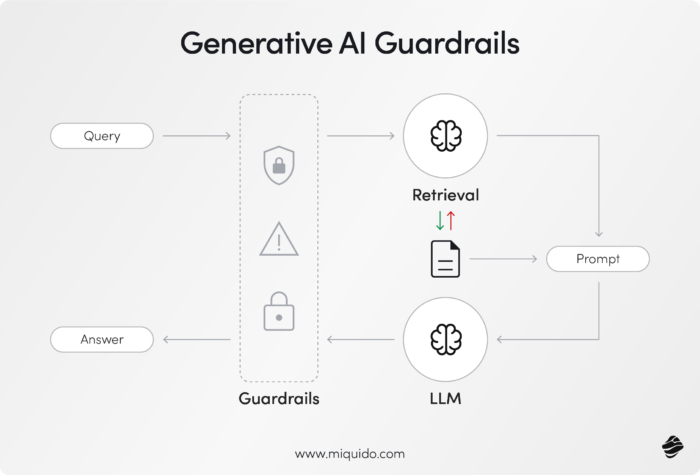
Generative AI guardrails are the built-in safety measures, guidelines, and restrictions that control and direct the behavior of AI systems. For generative AI technologies – like GPT, Gemini, and other large language models – these guardrails ensure outputs are ethical, accurate, and non-harmful. AI guardrails are necessary to safeguard AI systems against issues like AI hallucinations (generating false or misleading content), privacy breaches, bias amplification, and cyberattacks.
In essence, generative AI guardrails act as a framework to help organizations create responsible, compliant, and high-performing AI systems. They provide an essential layer of protection in sensitive applications, such as healthcare, finance, and customer interactions, ensuring the AI aligns with regulatory standards and business objectives.
What Are Guardrails in AI?
The primary goal of generative AI guardrails is ensuring ethical and responsible AI systems that operate safely and within the boundaries of societal norms and regulations. As generative AI continues to advance and become widely adopted in industries like healthcare, finance, and content creation, these guardrails are crucial for maintaining trust, reliability, and fairness. They address challenges such as:
- Preventing Harmful Outputs: Avoiding the creation of offensive, toxic, or misleading content.
- Minimizing Bias: Detecting and correcting AI bias in AI-generated outputs to promote fairness and inclusivity.
- Data Privacy: Ensuring sensitive information, such as personal identifiable information (PII), is protected and compliant with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
- Ethical Behavior: Aligning AI-generated outputs with human values and ethical standards to prevent misuse, such as disinformation or malicious applications.
Key Features of Generative AI Guardrails
Building AI guardrails solutions involves addressing technical, operational, and legal challenges. Advanced engineering and robust testing are crucial for managing technical issues, while collaboration among various teams is essential for operational integration. Additionally, adhering to evolving legal regulations adds complexity to the development process.
1. Toxicity Filters
Toxicity filters are used to detect and block harmful, offensive, or inappropriate language in AI outputs. They are especially critical in applications like chatbots, content creation tools, and social media platforms to ensure user safety and content moderation by validating both user inputs and LLM responses.
2. Bias Detection and Mitigation
Generative AI models trained on biased data may unintentionally replicate or amplify societal biases. Deep learning models play a crucial role in addressing these biases by integrating real-time bias detection tools that identify and adjust biased outputs, ensuring fairness and equity across all interactions.
3. Data Privacy Protections
AI guardrails automatically detect and apply data anonymization to sensitive information, such as names, addresses, or credit card numbers, to comply with privacy laws and maintain user trust. These safeguards are essential in regulated industries like finance and healthcare, where data security is paramount.
4. Content Verification Systems
These systems validate AI-generated outputs against trusted sources or datasets to ensure accuracy and reliability. For instance, a generative AI model tasked with providing legal advice or summarizing news articles would cross-check its output with verified data to prevent misinformation.
5. Cybersecurity Measures
Guardrails also protect AI systems from cyberattacks, such as prompt injection attacks, where bad actors try to manipulate the AI’s behavior. Advanced security mechanisms ensure the system remains reliable, secure, and resistant to external threats by operating within legal and technical boundaries.
Applications of Generative AI Guardrails
Generative AI guardrails are applied across industries and use cases to ensure safety, compliance, and reliability in various AI applications.
- Healthcare: Prevent AI systems from generating incorrect medical advice or violating patient privacy by incorporating HIPAA-compliant data handling guardrails.
- Finance: Ensure AI-generated reports, fraud detection models, or financial predictions align with industry regulations and ethical practices.
- Content Creation: Enforce brand tone and personality while blocking toxic or inappropriate content in text or image generation.
- Education: Validate AI-generated learning materials against trusted academic sources to ensure factual accuracy.
- Customer Service: Prevent AI chatbots from producing harmful or insensitive responses by incorporating real-time toxicity filters and brand voice enforcement.
Challenges in Implementing Generative AI Guardrails
While essential, building effective guardrails for generative AI comes with unique ethical, legal, and technical challenges:
- Complexity of AI Models: Large generative AI models, like GPT-4 or Gemini, are highly complex, making it difficult to predict or regulate every possible harmful outcome.
- Balancing Creativity with Control: Guardrails must be carefully designed to avoid stifling the AI’s creativity or potential for innovation. Overly restrictive guardrails could limit the system’s usefulness.
- Evolving Threats: As generative AI evolves, so do the risks, such as deepfake technology and misinformation. Guardrails need to adapt to address emerging challenges effectively.
- Interpretability Issues: Many guardrail mechanisms operate as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand or explain how they work, which can pose challenges in highly regulated industries.
Examples of Generative AI Guardrails in Action
- Toxicity Filters for Chatbots: AI chatbots powered by models like GPT-4 include toxicity filters to ensure responses remain safe and appropriate. For instance, a chatbot in a mental health app would block harmful advice or language. Ensuring a positive user experience is crucial as errors and issues with AI can negatively impact user experience, which in turn threatens the brand reputation of companies utilizing these AI systems.
- Bias Mitigation in Hiring Tools: Generative AI used in recruitment is equipped with bias detection guardrails to ensure recommendations for candidates are fair, inclusive, and free from discriminatory biases.
- Data Privacy in Healthcare AI: Healthcare applications using AI integrate guardrails to anonymize patient data, ensuring compliance with HIPAA while maintaining the AI’s ability to provide accurate insights.
- Fact-Checking Tools in News Generation: AI systems generating news summaries validate content against trusted sources using content verification guardrails to prevent the spread of misinformation.
The Importance of Guardrails in Responsible AI Development
As AI technology becomes increasingly pervasive, understanding why AI guardrails are essential cannot be overstated. These safeguards are critical to fostering trust, protecting users, and ensuring that AI systems align with ethical, legal, and societal standards. Here’s why they matter:
- Maintaining Trust: Trustworthy AI systems encourage adoption and confidence among users and businesses.
- Preventing Harm: Robust guardrails reduce risks of AI-generated outputs causing emotional, psychological, or financial harm.
- Ensuring Compliance: Guardrails help organizations avoid legal penalties by adhering to regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
- Driving Innovation Safely: Guardrails ensure that innovation in AI progresses responsibly, balancing creativity with safety.
The Future of Generative AI Guardrails
The development of AI guardrails is an ongoing process, as new challenges and risks continue to emerge. Future advancements are expected to include:
- Explainable AI (XAI): Guardrails will increasingly include transparency features to help users understand how decisions are made.
- Human In The Loop: Incorporating human oversight into AI outputs to refine and improve system performance.
- Universal Standards: Establishing global frameworks and guidelines to ensure consistency in AI safety measures across industries.
Additionally, there is a continuous need for mitigating risks in generative AI by addressing issues such as bias in training data, privacy concerns, and the potential for misuse.
In Summary
Generative AI guardrails play a crucial role in creating safe, ethical, and reliable AI systems. By incorporating features like bias detection, content validation, and cybersecurity measures, these guardrails ensure that AI outputs align with human values and regulatory requirements. As generative AI continues to grow in capability and impact, guardrails will play a pivotal role in shaping its responsible adoption and use across industries.
Ready to discover more terms?







