NLI: Natural Language Inference Definition
What is Natural Language Inference (NLI)?
Natural Language Inference (NLI) is a machine learning task that helps computers understand human language. NLI contributes to the semantic understanding of text by enabling machines to grasp the meaning and context of language. It is a critical task within the broader field of natural language processing (NLP), involving the analysis of a given statement (premise) and deciding whether another statement (hypothesis) is true (entailment), false (contradiction), or uncertain (neutral) based on the premise. NLI is important for improving how machines process and interpret language, similar to how humans draw conclusions from information.
As AI models continue to advance, NLI plays a key role in enhancing reasoning capabilities within large language models (LLMs). Recent innovations, such as GPT-4, Claude, Gemini, and Mistral, have significantly improved AI’s ability to understand and interpret complex text.
How Recognizing Textual Entailment Works
NLI is based on analyzing the logical inference and inference relation between sentence pairs to determine their logical relationship. Advanced deep learning models trained on large-scale datasets enable AI to perform these inferences more accurately.
Key Components of NLI
- Premise: The given statement that serves as the foundation.
- Hypothesis: A second statement evaluated against the premise.
- Label: The classification of the hypothesis in relation to the premise.
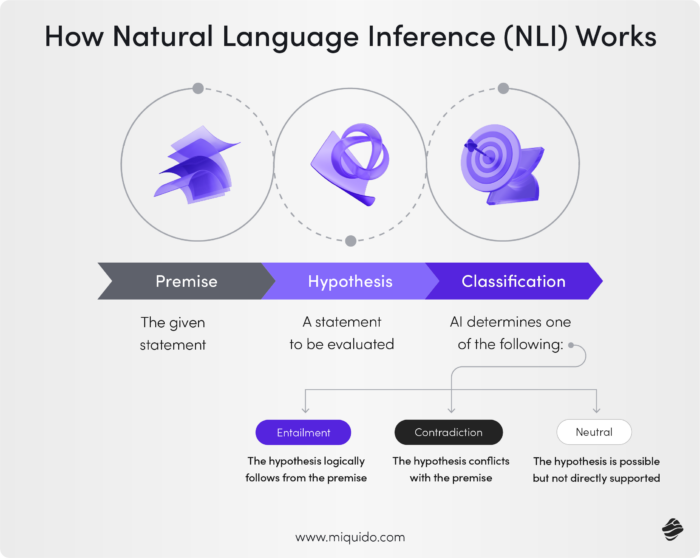
NLI Categories with Examples
Let’s explore the three main categories of NLI with practical examples:
Recognizing textual entailment is the task of determining the logical relationship between texts. It involves classifying the relationship as entailment, contradiction, or neutral.
- Entailment (True Hypothesis)
- Premise: “The dog is sleeping on the couch.”
- Hypothesis: “The dog is resting.”
- Classification: Entailment (The hypothesis logically follows from the premise.)
- Contradiction (False Hypothesis)
- Premise: “A man is eating a salad.”
- Hypothesis: “The man is fasting.”
- Classification: Contradiction (The hypothesis conflicts with the premise.)
- Neutral (Uncertain Hypothesis)
- Premise: “A woman is reading a book in the park.”
- Hypothesis: “The woman enjoys mystery novels.”
- Classification: Neutral (The hypothesis is possible but not directly supported by the premise.)
By classifying statements into these categories, NLI enables AI models to better understand and interpret language, improving their ability to draw logical conclusions from text. By classifying statements into these categories, NLI enhances the contextual understanding of AI models, enabling them to draw logical conclusions from text.
How NLI Models Are Trained
Modern NLI models require large, diverse datasets containing sentence pairs and their logical relationships. Data augmentation techniques are often used to expand these datasets, providing more varied examples for training. A significant natural language inference dataset is the Stanford Natural Language Inference (SNLI), which serves as a benchmark for evaluating models’ capabilities in understanding and inferring sentence relationships. Other widely used NLI datasets include:
- Multi-Genre Natural Language Inference (MNLI): A broader dataset covering various writing styles.
- Question Natural Language Inference (QNLI): Designed for question-answering systems.
- ANLI (Adversarial NLI): Includes harder examples to improve robustness in AI reasoning.
Training Process of NLI Models
- Preprocessing – Tokenizing sentences and removing irrelevant data.
- Feature Extraction – Converting words into vector representations using modern embeddings (e.g., OpenAI’s embeddings, LLaMA-based models, and Gemini’s advanced token representations).
- Deep Learning Training – Transformer models analyze sentence relationships and learn to classify them into entailment, contradiction, or neutral.
- Evaluation & Fine-Tuning – Models are tested on unseen data and optimized for higher accuracy. The process of containerizing natural language inference models using Docker involves building and running Docker images that contain these models, including how to display performance metrics.
The emergence of advanced LLMs like GPT-4, Claude, and Gemini has drastically improved NLI performance. These models can generalize across diverse text sources, making them more effective at understanding logical relationships.
Applications of Natural Language Inference
NLI is widely used in AI applications that require logical reasoning, text analysis, and decision-making. Textual entailment, a critical task within natural language processing (NLP), plays a significant role in determining the logical relationship between two text segments, classifying them as entailment, contradiction, or neutral. This method is essential in various NLP applications like question-answering and sentiment analysis.

NLI also enhances semantic search capabilities, allowing search engines to retrieve more relevant content based on the meaning and context of queries.
1. Conversational AI and Chatbots
NLI enhances chatbots and virtual assistants (e.g., ChatGPT, Claude, and Google Bard) by:
- Verifying whether a response aligns with a user’s question.
- Detecting contradictions or inconsistencies in user input.
- Generating more context-aware and logically consistent replies.
2. Search Engines and Information Retrieval
NLI improves search engines (e.g., Google Search, Perplexity AI) by:
- Identifying relevant search results based on intent, not just keywords.
- Enhancing semantic search capabilities for better content retrieval.
3. Fake News Detection and Fact-Checking
NLI aids automated fact-checking systems in:
- Comparing claims against trusted sources.
- Detecting contradictions or misinformation in articles and social media content.
4. Machine Translation Evaluation
NLI helps in assessing translations by:
- Checking if the translation preserves the original meaning.
- Detecting errors or contradictions in machine-generated translations.
5. Automated Summarization
NLI-powered summarization tools ensure that:
- Generated summaries accurately reflect key points of the original text.
- No misleading or contradictory information is introduced.
Challenges and Future of NLI
Despite its progress, NLI still faces challenges:
Improving the robustness of NLI models is crucial to ensure they can handle diverse and complex language inputs.
1. Handling Ambiguity and Context
- Understanding sarcasm, idioms, or vague language remains difficult.
- Sentences requiring deep reasoning can still be misclassified.
2. Bias in Training Data
- If datasets contain biased language patterns, models may inherit these biases.
- Ethical AI principles and diverse training data can help mitigate bias.
3. Scalability for Multilingual AI
- While English-based NLI models perform well, multilingual models require more development.
- Expanding datasets across languages is crucial for global AI applications.
Future Developments
- Few-shot and Zero-shot Learning: AI models will require less training data to understand inference.
- Explainable AI in NLI: Improving AI interpretability will enhance trust in its decisions.
- Multimodal NLI: Future systems will analyze text, images, and videos together for deeper understanding.
- Integration with Autonomous Agents: NLI will power reasoning in AI agents that perform complex decision-making.
As AI research advances, NLI will continue to shape the development of intelligent, context-aware systems, making AI more human-like in its reasoning and comprehension.
Natural Language Inference: Definition Overview
Natural Language Inference (NLI) is a foundational task in machine learning that enables AI to logically interpret human language. By categorizing text relationships into entailment, contradiction, and neutrality, NLI enhances applications such as chatbots, search engines, fact-checking, and text summarization.
With advancements in deep learning, large-scale LLMs, and multilingual AI, NLI is evolving toward more accurate, bias-free, and scalable solutions. As we move forward, AI’s ability to reason and infer meaning will continue to improve, bringing us closer to truly intelligent language understanding.
Ready to discover more terms?

![[header] how is ai used in the music industry overcoming trust, fraud & transparency challenges with ai](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/header-how-is-ai-used-in-the-music-industry_-overcoming-trust-fraud-transparency-challenges-with-ai-432x288.jpg)