- Home
- AI Glossary
- Discriminative AI Definition


Discriminative AI Definition
Discriminative AI Definition
What is Discriminative AI?
Discriminative AI refers to a class of artificial intelligence (AI) models designed to distinguish between different types of data inputs by learning the boundaries between predefined categories. Unlike generative AI, which creates new data instances (e.g., images or text), discriminative AI analyzes and classifies existing data by estimating the conditional probability distribution of output labels given input data.
These models are trained to differentiate between classes in a dataset rather than generate new samples. For example, a discriminative AI model in image recognition determines whether an image contains a cat or a dog, while a generative model could create a completely new image of a cat.
Where is Discriminative AI Used?
Discriminative AI plays a crucial role in classification and pattern recognition across multiple industries:
- Image Recognition: Identifying objects in photos, such as distinguishing between different species in wildlife photography.
- Speech Recognition: Converting spoken language into text by classifying sound patterns.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Used in spam detection, sentiment analysis, and chatbot responses.
- Healthcare: Assisting in disease diagnosis by classifying medical images or lab results.
- Finance: Enhancing fraud detection by distinguishing between legitimate and fraudulent transactions.
- Retail & Marketing: Analyzing customer preferences to improve personalized recommendations.
Correctly classifying each data point is crucial in applications like image recognition and speech recognition, as misclassifying a single data point can lead to significant errors in the model’s predictions.
How Does Discriminative AI Work?
Discriminative AI models learn through supervised learning, where they are trained on labeled datasets to recognize distinct patterns and decision boundaries based on the input data. The process involves:
- Training on Labeled Data: The model is fed labeled training data (e.g., images labeled as “cat” or “dog”).
- Feature Extraction: It learns key features that differentiate classes, such as fur texture or shape.
- Decision Boundary Formation: The model defines boundaries to separate different classes based on learned features.
- Classification of New Data: When given unseen data, the model applies its learned patterns to correctly classify the input based on the identified data points.
Popular machine learning algorithms used in discriminative AI include:
- Logistic Regression – for binary classification tasks.
- Support Vector Machines (SVMs) – to create decision boundaries.
- Neural Networks (e.g., CNNs, RNNs) – for deep learning applications like image and speech recognition.
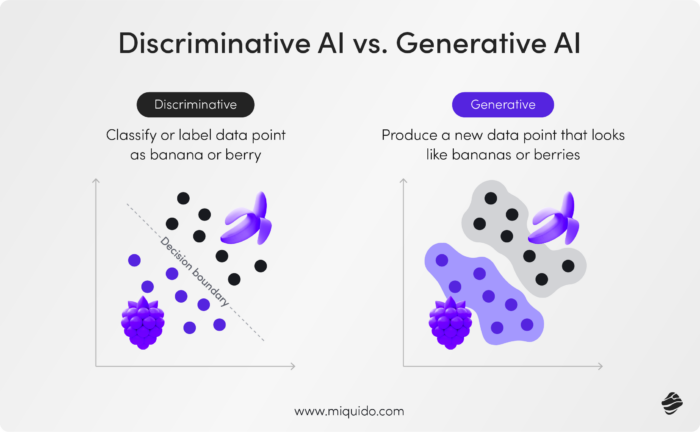
Discriminative AI Definition vs. Generative Models Definition
| Feature | Discriminative AI | Generative AI |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Classifies data into predefined categories | Creates new data instances using generative and discriminative models |
| Example | Distinguishing between cat and dog images | Generating a new image of a cat using generative models |
| Common Algorithms | Logistic Regression, SVMs, Neural Networks | Generative adversarial networks (GANs), VAEs, Transformer models |
| Application Areas | Image classification, NLP, fraud detection | AI-generated art, text generation, synthetic data creation |
When comparing generative AI vs discriminative AI, it is important to understand their different approaches. Generative AI utilizes the joint probability distribution of input data and labels to create new data. It focuses on capturing the complexities of the underlying data distribution. This allows for effective data generation, creating new instances that resemble the original dataset.
The Future of Discriminative AI
As AI technology advances, discriminative models are becoming more precise and efficient, integrating with deep learning for enhanced accuracy. They are increasingly used in real-time applications, such as autonomous vehicles, cybersecurity, and medical diagnostics, where accurate classification is critical.
With ongoing innovations in AI ethics and bias reduction, future discriminative AI models will be more transparent, fair, and interpretable, ensuring responsible AI development in diverse industries. Additionally, these models will play a crucial role in modeling data points for future applications, enhancing the understanding and performance of machine learning algorithms.
What is Discriminative AI?
Discriminative AI represents a specialised area in artificial intelligence focused on distinguishing between different types of data inputs. At its core, Discriminative AI refers to models that learn the boundaries between different classes in a dataset. Unlike generative AI models that create new data instances, discriminative AI relies on existing data, identifying and categorizing it based on learned patterns.
Where is Discriminative AI used?
A key aspect of discriminative AI is its application in tasks like image recognition, speech recognition, and natural language processing. The AI analyses input data (like photos, audio, or text) and classifies it into predefined categories. For instance, a discriminative AI might determine in image recognition whether a picture contains a cat or a dog. This classification ability makes discriminative AI invaluable in various sectors, including healthcare for diagnostic tools, finance for fraud detection, and retail for customer preference analysis.
How does Discriminative AI work?
Underlying the operation of discriminative AI are algorithms that learn from a set of training data. This training involves feeding the AI examples (like pictures of cats and dogs) until it learns to distinguish between them. The more data it processes, the more accurate it becomes.
These models learn from examples, and the quality of their output heavily depends on the diversity and volume of the data they are trained on. A well-trained Discriminative AI can be incredibly effective in correctly classifying new, unseen data.
As technology evolves, the importance of Discriminative AI continues to grow. Its application spans diverse fields, constantly pushing the boundaries of what AI can achieve in terms of accuracy and reliability. In the evolving landscape of technology, we can expect discriminative AI to become even more sophisticated, offering more precise and reliable classifications across a broader range of applications.
Ready to discover more terms?